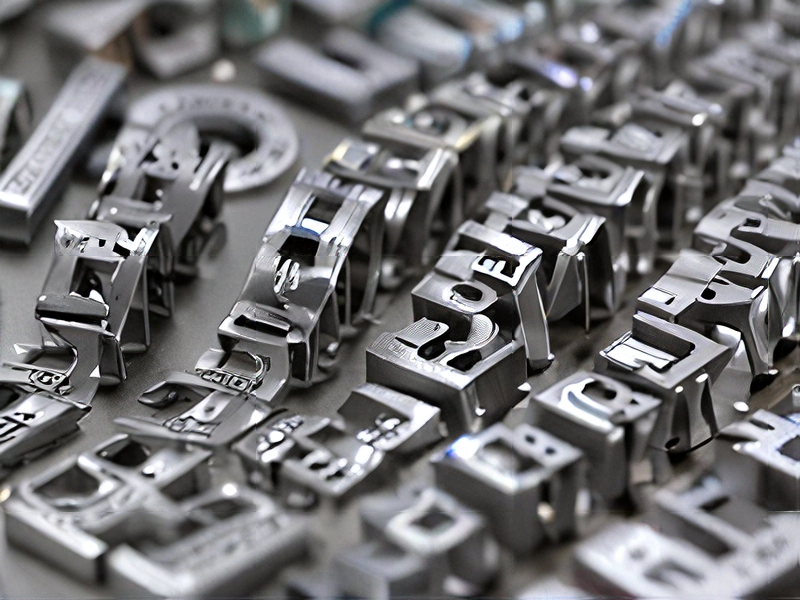
Technology and Applications of 3d metal printing service
3D metal printing, or additive manufacturing, has transformed manufacturing by allowing for the production of complex metal parts with high precision and minimal waste. The technology primarily includes methods like Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Electron Beam Melting (EBM), and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS).
Technology:
1. Selective Laser Melting (SLM): Uses a high-power laser to melt and fuse metallic powders layer by layer. This method is ideal for creating intricate geometries and has applications in aerospace and medical industries.
2. Electron Beam Melting (EBM): Utilizes an electron beam under a vacuum to melt metal powder. It’s faster than SLM and suitable for high-temperature materials like titanium, used in aerospace and medical implants.
3. Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): Similar to SLM but typically involves sintering rather than fully melting the powder, allowing for a wider range of alloys to be used.
Applications:
1. Aerospace: 3D metal printing allows for the creation of lightweight, strong parts with complex geometries that traditional methods can’t achieve. This results in more efficient fuel usage and reduced emissions.
2. Medical: Custom implants and prosthetics can be tailored to individual patients, improving the fit and function. For instance, 3D printing enables the production of porous structures that promote bone growth.
3. Automotive: Rapid prototyping and the production of high-performance components such as engine parts and custom tools are streamlined through 3D metal printing.
4. Industrial Manufacturing: Production of specialized machinery parts, tools, and fixtures that are custom-made for specific applications, enhancing operational efficiency.
3D metal printing reduces material waste and allows for the on-demand production of parts, which can significantly lower inventory costs and lead times. As technology advances, it’s expected to further revolutionize industries by offering unprecedented customization and efficiency.
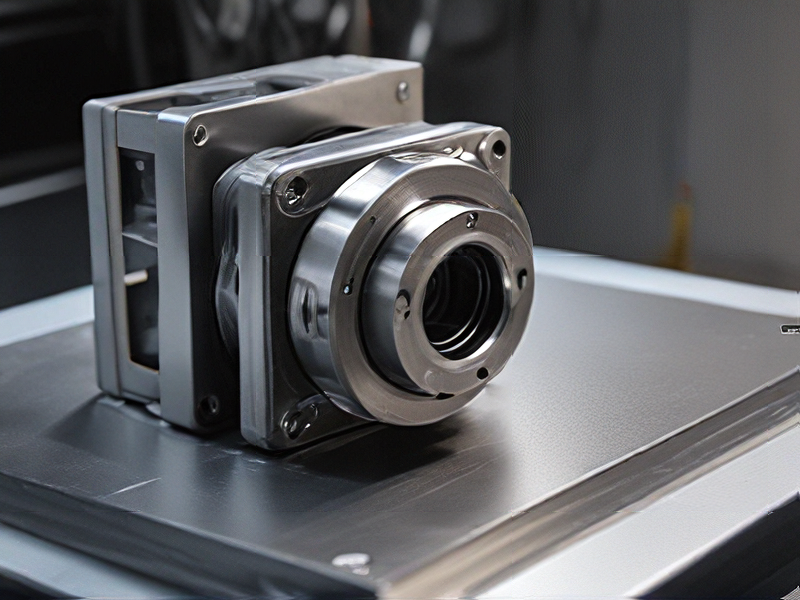

Quality Testing Methods for 3d metal printing service and how to control quality
Quality testing methods for 3D metal printing services typically include several key approaches to ensure the final products meet required standards:
1. Visual Inspection: Initial assessment for surface defects, layer uniformity, and overall finish.
2. Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) or laser scanners to verify dimensional accuracy against CAD models.
3. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as X-ray or CT scanning to detect internal defects like voids or cracks without damaging the part.
4. Mechanical Testing: Assessing mechanical properties through tests like tensile, hardness, or impact tests to ensure parts meet strength and durability requirements.
5. Microstructural Analysis: Examining the microstructure using metallographic techniques to ensure proper grain structure and absence of defects at a microscopic level.
To control quality effectively:
– Process Optimization: Regular calibration and maintenance of 3D printers, ensuring parameters like temperature and printing speed are consistently controlled.
– Material Control: Monitoring and verifying the quality of metal powders or filaments used in printing.
– Documentation and Traceability: Maintaining detailed records of process parameters, material batches, and testing results for traceability and continuous improvement.
– Certification and Standards Compliance: Adhering to industry standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO) for specific applications or sectors.
By implementing these methods and controls, 3D metal printing services can ensure high-quality parts suitable for a range of applications from aerospace to medical industries.
Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from 3d metal printing service
When considering procurement from a 3D metal printing service, several key factors should guide your decision-making process:
1. Quality Standards: Ensure the service provider meets industry standards for 3D metal printing. Look for certifications like ISO 9001 which ensure quality management systems are in place.
2. Technology and Capabilities: Evaluate the types of 3D metal printing technologies the service provider offers (e.g., Direct Metal Laser Sintering, Selective Laser Melting) and their ability to handle your project’s specifications such as size, complexity, and material requirements.
3. Material Options: Check if the service provider offers a range of metal materials suitable for your application (e.g., stainless steel, titanium, aluminum). Consider their expertise in handling these materials and any specific material properties you need.
4. Experience and Reputation: Review the provider’s track record and customer testimonials to gauge their reliability, consistency, and ability to deliver on time.
5. Post-Processing Capabilities: Assess what post-processing services are available, such as machining, heat treatment, or surface finishing, to ensure your parts meet final specifications.
6. Cost and Value: Compare pricing structures among different providers while considering factors like setup fees, material costs, and any additional services. Ensure transparency in pricing and potential cost savings through bulk orders or ongoing contracts.
7. Lead Times and Flexibility: Understand typical lead times for production and delivery. Flexibility in accommodating rush orders or adjustments to designs can be crucial.
8. Communication and Support: Clear communication channels and responsive customer support are essential for addressing queries, providing updates, and resolving any issues promptly.
9. Intellectual Property Protection: Ensure the service provider has measures in place to protect your designs and intellectual property throughout the production process.
10. Environmental Considerations: Evaluate the provider’s sustainability practices, such as material recycling or energy-efficient manufacturing processes, if environmental responsibility is a priority for your organization.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select a 3D metal printing service provider that aligns with your project requirements and ensures quality, reliability, and efficiency in procurement.
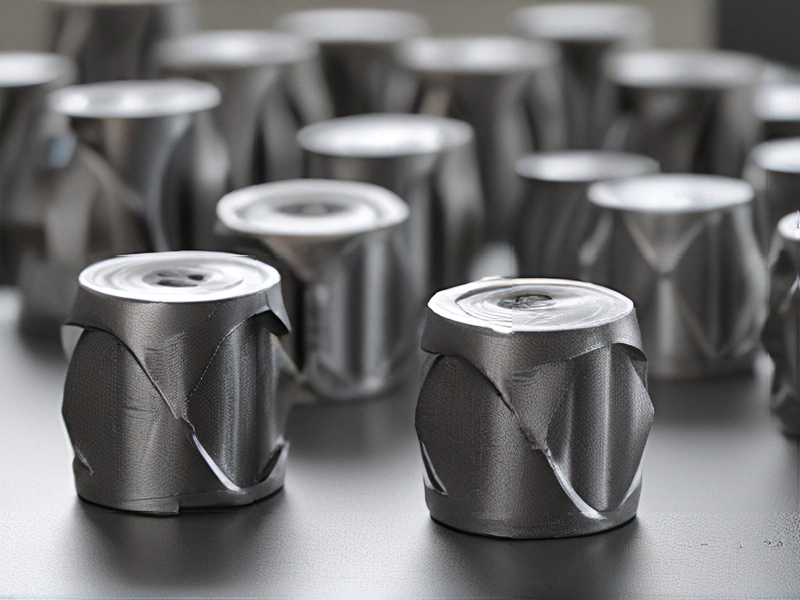

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from 3d metal printing service in China
Certainly! Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) regarding sourcing and manufacturing from a 3D metal printing service in China:
1. What types of metals can be 3D printed?
3D metal printing services in China typically work with a range of metals including stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and nickel alloys.
2. What are the advantages of using 3D metal printing?
3D metal printing allows for complex geometries, rapid prototyping, and customization without the need for traditional tooling. It can also reduce material waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
3. How can I ensure quality in 3D metal printed parts?
Ensure the service provider has certifications like ISO 9001 and AS9100, which indicate adherence to quality standards. Request samples or visit facilities if possible to inspect equipment and processes.
4. What is the typical lead time for 3D metal printing orders?
Lead times can vary based on part complexity, size, and material. Generally, smaller and less complex parts have shorter lead times, ranging from days to a few weeks.
5. Are there any restrictions on part size or complexity?
Some 3D metal printers have limitations on maximum build size and intricate features. Discuss your design requirements with the service provider to ensure compatibility with their equipment.
6. What post-processing services are offered?
Services may include heat treatment, surface finishing (polishing, painting), and machining to achieve desired specifications and surface quality.
7. What are the shipping and logistics options for international orders?
Providers often have partnerships with logistics companies to facilitate international shipping. Discuss packaging, insurance, and shipping methods (air vs. sea) to optimize cost and delivery time.
8. How does pricing work for 3D metal printing services?
Pricing depends on factors such as material choice, part complexity, volume, and post-processing requirements. Request a detailed quote based on your specific project parameters.
9. What intellectual property (IP) protections are in place?
Ensure the service provider respects confidentiality and IP rights. Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) can be signed to protect proprietary designs and information.
10. Can the service provider handle large-scale production orders?
Verify production capabilities and capacity to meet your volume requirements. Some providers specialize in prototyping while others can handle larger production runs.
These FAQs should provide a solid foundation for understanding and navigating sourcing and manufacturing through a 3D metal printing service in China.

