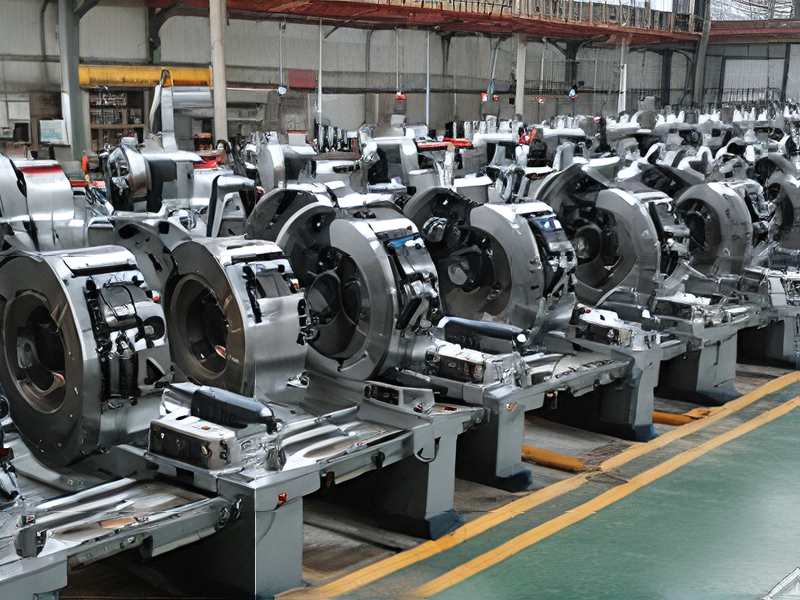
Technology and Applications of c and c machines
Technology and Applications of CNC Machines
Technology:
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines utilize computerized controls to operate and manipulate machine tools, such as lathes, mills, routers, and grinders. The technology involves converting a computer-aided design (CAD) into a precise set of instructions (G-code) that the CNC machine follows to produce parts with high accuracy and repeatability. Key components include:
– Controller: The brain of the CNC machine, executing programmed instructions.
– Drive System: Translates signals from the controller into precise movements.
– Feedback System: Monitors and adjusts the machine’s position and velocity.
Applications:
1. Manufacturing:
– Automotive: CNC machines are used to create engine components, transmission parts, and custom car parts.
– Aerospace: Essential for producing complex parts like turbine blades, airframe components, and landing gear.
– Electronics: Used to manufacture circuit boards and electronic enclosures.
2. Medical:
– Prosthetics and Implants: Precision machining of custom prosthetics and orthopedic implants.
– Surgical Instruments: Production of high-precision surgical tools.
3. Construction:
– Structural Components: Fabrication of steel beams and concrete molds.
– Custom Fixtures: Creation of bespoke architectural elements.
4. Furniture and Woodworking:
– Custom Furniture: CNC routers create detailed wood designs and furniture components.
– Cabinetry: Precision cutting and engraving for cabinets and decorative pieces.
5. Art and Design:
– Sculptures and Models: Artists use CNC machines for intricate sculptures and scale models.
– Jewelry Making: Crafting detailed and precise jewelry pieces.
CNC machines revolutionize manufacturing by offering high precision, repeatability, and efficiency, catering to industries requiring complex and detailed production processes.
Quality Testing Methods for c and c machines and how to control quality
Quality Testing Methods for CNC Machines
1. Dimensional Accuracy Testing:
– Dial Indicators: Measure linear and rotational accuracy.
– Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM): Inspect complex geometries and dimensions.
– Laser Interferometry: Assess positioning accuracy and repeatability.
2. Surface Finish Testing:
– Profilometers: Gauge surface roughness.
– Visual Inspection: Identify defects and irregularities.
3. Material Testing:
– Hardness Tests: Evaluate the material’s resistance to deformation.
– Tensile Testing: Determine the material’s strength and ductility.
4. Machine Calibration:
– Ball Bar Test: Check geometric accuracy and detect errors.
– Renishaw Machine Checking Gauge: Assess the machine’s performance over its working envelope.
Quality Control Methods
1. Statistical Process Control (SPC):
– Use control charts to monitor process variation.
– Identify trends and apply corrective actions before defects occur.
2. Regular Maintenance and Calibration:
– Schedule periodic maintenance to ensure consistent machine performance.
– Perform regular calibration to maintain accuracy.
3. Training and Certification:
– Ensure operators are well-trained in machine operation and quality standards.
– Provide ongoing training to keep up with technological advancements.
4. Documentation and Traceability:
– Maintain detailed records of each production batch.
– Implement traceability to track and address defects back to their source.
5. Automated Quality Control Systems:
– Integrate sensors and cameras to automatically inspect and measure parts.
– Use software to analyze data and provide real-time feedback.
By employing these methods, CNC machine quality can be effectively tested and controlled, ensuring high precision and reliability in manufacturing processes.

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from c and c machines
When procuring from C and C Machines, consider these tips to ensure a smooth and beneficial purchasing process:
1. Understand Your Requirements:
– Clearly define what you need, including machine specifications, capabilities, and any unique requirements specific to your operations.
– Evaluate whether C and C Machines’ offerings align with your technical and operational needs.
2. Supplier Research:
– Investigate C and C Machines’ reputation in the market. Look for reviews, testimonials, and case studies from other customers.
– Verify their financial stability and track record in delivering quality products.
3. Quality and Compliance:
– Ensure the machines comply with industry standards and certifications.
– Request information about the quality control processes they have in place.
4. Cost Considerations:
– Obtain detailed quotations, including hidden costs such as shipping, installation, and maintenance.
– Compare these costs with other suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
5. After-Sales Support:
– Assess the availability and quality of after-sales support, including maintenance services, spare parts, and technical support.
– Check if they offer training for your team to effectively operate and maintain the machines.
6. Delivery and Installation:
– Confirm the lead times for delivery and the logistics involved.
– Ensure they provide professional installation services and initial setup assistance.
7. Warranty and Service Agreements:
– Scrutinize the warranty terms and conditions.
– Negotiate service agreements to cover maintenance and repairs beyond the warranty period.
8. Sustainability and Innovation:
– Consider the energy efficiency and environmental impact of the machines.
– Evaluate the company’s commitment to innovation and technological advancements.
By meticulously assessing these factors, you can make an informed decision and secure machinery that enhances productivity and aligns with your operational goals.
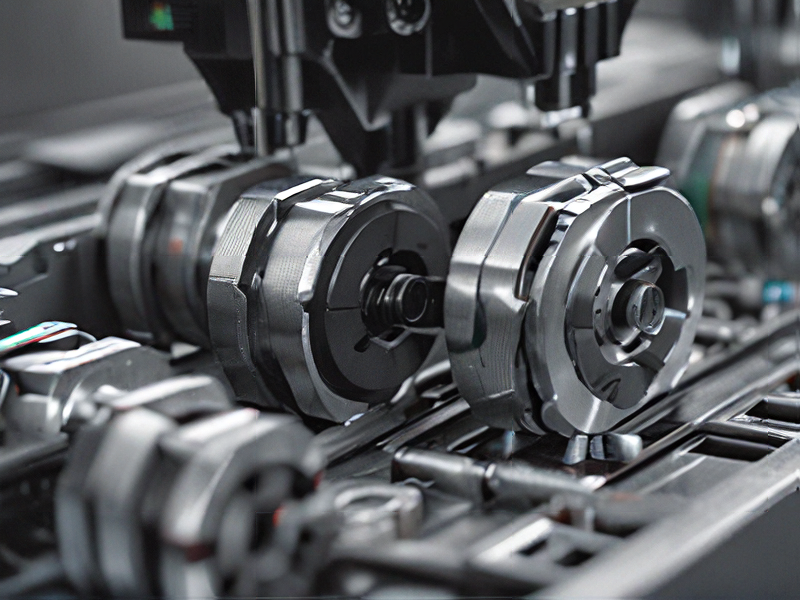

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from c and c machines in China
Certainly! Here are some FAQs regarding sourcing and manufacturing from CNC machines in China:
1. What are the advantages of sourcing CNC machining from China?
China offers cost-effective manufacturing due to lower labor and production costs. It also boasts a wide range of suppliers with advanced CNC technology.
2. How can I find reliable CNC machine suppliers in China?
Utilize online platforms like Alibaba or Made-in-China.com, and conduct thorough supplier vetting. Consider reviews, certifications, and request samples or factory visits.
3. What are the typical lead times for CNC machining orders from China?
Lead times vary but can range from a few days for simple parts to several weeks for complex assemblies. Factors include part complexity, quantity, and supplier capacity.
4. How do I ensure quality when sourcing CNC machining from China?
Specify detailed technical requirements, conduct quality inspections during production, and consider third-party quality control services. Establish clear communication channels with the supplier.
5. What are the common challenges when manufacturing in China?
Challenges may include language barriers, cultural differences, intellectual property concerns, and logistics management. Effective communication and thorough contracts can mitigate these risks.
6. What are the payment terms typically used with Chinese CNC machining suppliers?
Payment terms can vary but often include a deposit upfront (30-50%) with the balance due upon completion and before shipping. Use secure payment methods and consider trade assurance options.
7. How can I manage logistics and shipping when manufacturing in China?
Work closely with your supplier to coordinate shipping methods, packaging requirements, and customs documentation. Consider using freight forwarders for efficient logistics handling.
By addressing these FAQs, businesses can navigate the complexities of sourcing and manufacturing from CNC machines in China effectively.

