Technology and Applications of laser cuts metal
Laser cutting technology has revolutionized metal fabrication by offering precision, speed, and versatility. It involves using a high-powered laser to cut through materials, primarily metals such as steel, aluminum, and titanium. The process works by directing the laser beam through a nozzle to the workpiece, where it melts or vaporizes the material along a predetermined path, known as the kerf.
Applications of laser cutting in metalwork span various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and jewelry manufacturing. Its ability to achieve intricate cuts with minimal material wastage makes it ideal for producing complex components like gears, brackets, and enclosures. In automotive manufacturing, laser cutting is used for producing chassis components and body panels with high accuracy and speed.
The technology’s flexibility allows for cutting different thicknesses of metal, ranging from thin foils to thick plates, without the need for tool changes. This adaptability is crucial in prototyping and custom fabrication where rapid iteration and precision are essential.
Advantages of laser cutting include high cutting speeds, minimal heat-affected zones, and the capability to cut reflective materials with ease. Moreover, its computer numerical control (CNC) integration enables automation and precise replication of designs, ensuring consistency in production.
In summary, laser cutting technology continues to redefine metal fabrication by offering efficiency, precision, and versatility across a wide range of industries, contributing to advancements in manufacturing processes and product design.
Quality Testing Methods for laser cuts metal and how to control quality
Quality testing methods for laser-cut metal typically include:
1. Visual Inspection: This involves examining the cut edges for smoothness, burrs, and any signs of discoloration or irregularities.
2. Dimensional Inspection: Using precision tools like calipers or coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to verify dimensions against design specifications.
3. Surface Roughness Measurement: Assessing the surface finish using profilometers or roughness testers to ensure it meets required standards.
4. Microscopic Examination: Utilizing microscopy to inspect the microstructure of the cut edge for any defects such as cracks or heat-affected zones.
5. Metallurgical Analysis: Conducting tests like hardness testing to assess the mechanical properties and integrity of the cut edge.
To control quality effectively:
– Process Parameters Control: Monitor and adjust laser power, speed, and focus to optimize cutting quality and consistency.
– Regular Maintenance: Keep the laser cutting equipment well-maintained to ensure it operates within specified tolerances.
– Operator Training: Train operators to understand and troubleshoot potential quality issues during the cutting process.
– Quality Management System: Implement a quality management system (QMS) that includes documentation, traceability, and corrective/preventive actions.
By integrating these methods and controls, manufacturers can maintain high-quality standards for laser-cut metal components, ensuring consistency, accuracy, and reliability in their products.
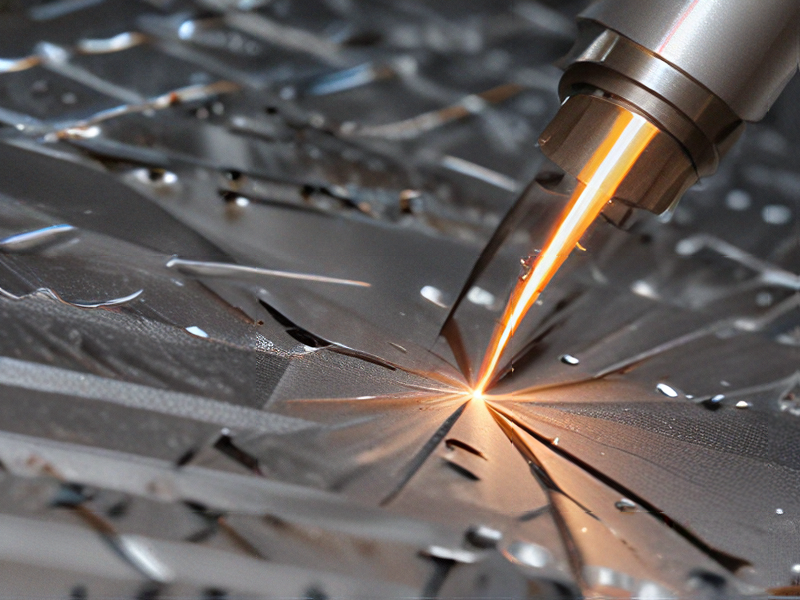

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from laser cuts metal
When procuring laser-cut metal, consider the following tips to ensure you receive high-quality products and value for your investment:
1. Supplier Evaluation: Research potential suppliers thoroughly. Look for reviews, certifications, and past project examples. Verify their experience with laser cutting and their capability to meet your specifications.
2. Material Quality: Ensure the metal used is of high quality and appropriate for your application. Common materials include stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel. Verify the material’s grade and thickness to match your needs.
3. Precision and Tolerances: Laser cutting is known for its precision. Confirm that the supplier can meet your required tolerances and has the necessary equipment to produce clean, accurate cuts without excessive burrs or defects.
4. Design and Customization: Provide clear, detailed CAD drawings of your design. Discuss any complex features or tight tolerances with the supplier to ensure they understand your requirements and can deliver as expected.
5. Volume and Lead Time: Communicate your order volume and required lead time upfront. Larger orders or custom designs may take longer, so plan accordingly. Ask about the supplier’s production capacity and their ability to scale if your demand increases.
6. Cost Considerations: Request detailed quotes, including material costs, cutting fees, and any additional charges. Compare multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing, but don’t sacrifice quality for cost savings.
7. Quality Control: Inquire about the supplier’s quality control processes. Ensure they perform regular inspections and provide quality assurance documentation. You may request samples before placing a large order.
8. Sustainability and Waste Management: Check if the supplier follows sustainable practices and efficient waste management. Eco-friendly operations can be a significant consideration for environmentally conscious businesses.
9. Logistics and Delivery: Consider the supplier’s location and delivery options. Efficient logistics can reduce lead times and shipping costs. Ensure they offer reliable and safe packaging to prevent damage during transit.
By following these tips, you can enhance your procurement process and secure high-quality laser-cut metal products that meet your specifications and business needs.

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from laser cuts metal in China
Certainly! Here are some FAQs regarding sourcing and manufacturing laser-cut metal in China:
1. How do I find a reliable manufacturer in China for laser-cut metal parts?
– Utilize online platforms like Alibaba or Made-in-China to search for manufacturers. Verify their credentials, read reviews, and request samples.
2. What factors should I consider when selecting a manufacturer?
– Quality standards, production capacity, turnaround times, communication proficiency, and adherence to international regulations like ISO certifications.
3. How can I ensure the quality of laser-cut metal parts produced in China?
– Specify detailed product requirements, conduct quality inspections during production, and request samples before mass production.
4. What are common challenges when manufacturing in China?
– Language barriers, cultural differences, intellectual property protection, and logistics issues such as shipping and import/export regulations.
5. How can I manage costs effectively?
– Obtain multiple quotes, negotiate pricing, consider economies of scale, and clarify all cost components including tooling, materials, and shipping.
6. What are typical lead times for laser-cut metal parts from China?
– Lead times can vary but typically range from a few weeks to a few months depending on complexity and order volume.
7. How do I handle intellectual property concerns when manufacturing in China?
– Utilize non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), clarify ownership rights, and consider patent protections in relevant jurisdictions.
8. What are the payment terms commonly used with Chinese manufacturers?
– Initial deposit (30-50%), with balance due upon completion or before shipment. Use secure payment methods to mitigate risks.
9. How do I ensure environmental and ethical standards are met?
– Choose manufacturers with certifications like ISO 14001 (environmental management) and audit their practices if possible.
10. What should I know about shipping logistics and import duties?
– Plan ahead for shipping times, understand import duties and taxes in your country, and consider using a freight forwarder for streamlined logistics.
Navigating these considerations can help ensure a successful partnership with a Chinese manufacturer for laser-cut metal parts.