Technology and Applications of router cnc projects
A router CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine is a cutting tool controlled by a computer, capable of carving, cutting, and shaping various materials such as wood, plastic, and metal. These machines have revolutionized manufacturing and craftsmanship by enhancing precision, efficiency, and repeatability in production.
Technology
Router CNC machines consist of several key components:
1. Controller: The brain of the CNC machine, interpreting design files (G-code) to direct the machine’s movements.
2. Spindle: The cutting tool’s motor, which rotates at high speeds to perform cutting operations.
3. Bed/Table: The surface on which materials are placed and secured during machining.
4. Drive System: Typically includes stepper or servo motors that move the spindle and bed along the X, Y, and Z axes.
5. Software: CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software for designing parts and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software for generating the G-code.
Applications
Router CNC machines are used in a variety of applications across different industries:
1. Furniture Making: Crafting intricate designs and components for furniture, such as decorative elements, joints, and panels.
2. Sign Making: Producing detailed signage, including 3D lettering and engraved logos.
3. Prototyping: Creating prototypes for product development in industries like automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods.
4. Custom Parts: Manufacturing custom components for machinery and equipment, often with complex geometries.
5. Art and Crafts: Producing artistic pieces, including sculptures, engravings, and detailed carvings.
Benefits
– Precision: High accuracy in cutting and shaping materials.
– Efficiency: Faster production times compared to manual methods.
– Consistency: Uniform results in repeated productions.
– Versatility: Ability to work with a wide range of materials and designs.
Router CNC technology continues to evolve, integrating advanced features like automation, IoT connectivity, and enhanced software capabilities, making it a cornerstone in modern manufacturing and artisanal projects.
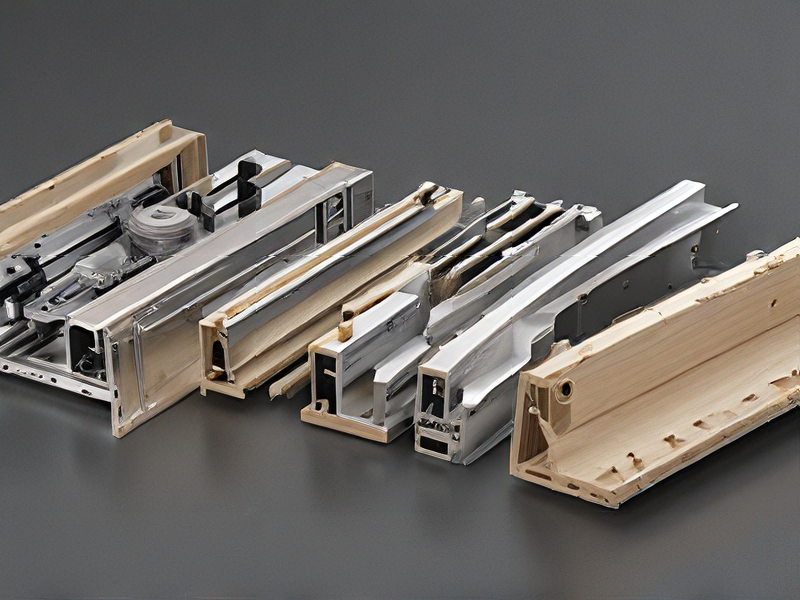

Quality Testing Methods for router cnc projects and how to control quality
To ensure high-quality CNC router projects, several testing methods can be employed:
1. Dimensional Accuracy Checks: Use calipers or measurement tools to verify dimensions against design specifications.
2. Surface Finish Assessment: Inspect surfaces for smoothness and any unintended tool marks using visual inspection or touch.
3. Material Integrity Testing: Conduct strength tests or stress tests on samples to ensure materials withstand intended use.
4. Functionality Testing: Run the finished part through simulations or assembly tests to confirm it fits and functions as intended.
5. Precision Testing: Utilize precision measuring instruments like micrometers or laser scanners to check for tolerances.
Controlling quality involves:
1. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Define clear steps for production and inspection to maintain consistency.
2. Quality Control Points: Implement checkpoints during production to catch defects early.
3. Employee Training: Ensure operators are trained in quality standards and equipment use.
4. Feedback Loops: Establish a system for collecting feedback from customers or internal teams to improve processes.
5. Documentation: Maintain records of inspections and tests to track quality over time and identify areas for improvement.
By integrating these methods and controls, manufacturers can consistently deliver high-quality CNC router projects that meet customer expectations.
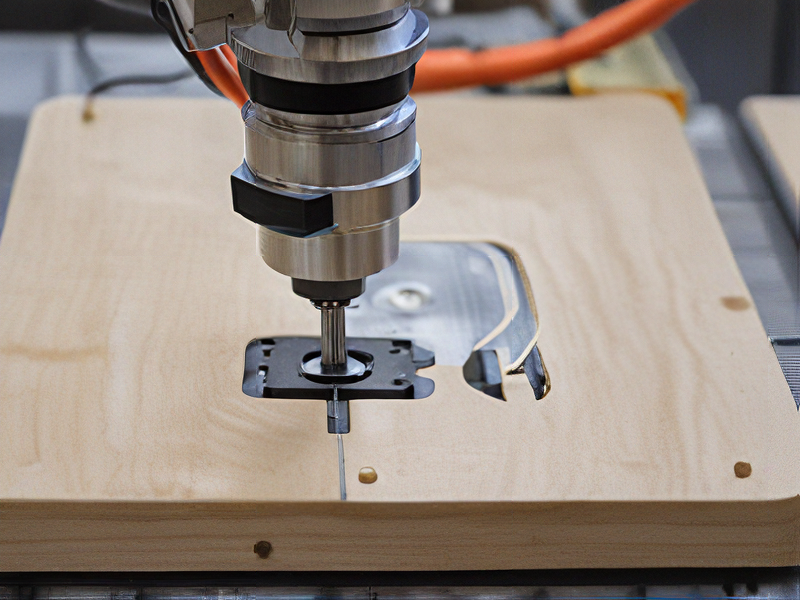

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from router cnc projects
When procuring materials or components for CNC router projects, several key tips and considerations can ensure successful outcomes:
Research and Quality
1. Vendor Reputation: Choose suppliers with a solid track record and positive reviews. Reliable vendors reduce the risk of receiving subpar materials.
2. Material Quality: Ensure the materials meet your project specifications in terms of durability, finish, and compatibility with your CNC router.
Cost and Budgeting
3. Compare Prices: Obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to get the best value for money. However, avoid compromising on quality for lower costs.
4. Bulk Purchasing: Buying in bulk can often result in discounts. Calculate your project needs accurately to benefit from bulk rates without over-purchasing.
Technical Specifications
5. Material Specifications: Check the exact specifications required for your project, such as thickness, hardness, and type of material (e.g., wood, aluminum, plastic).
6. Compatibility: Ensure the materials are compatible with your CNC router’s capabilities, including spindle speed, cutting tools, and software requirements.
Supplier Services
7. Lead Times: Confirm the supplier’s delivery times to avoid project delays. Reliable lead times are crucial for project scheduling.
8. Customer Support: Good customer support can assist with technical queries and post-purchase issues, enhancing the procurement experience.
Quality Assurance
9. Samples: Request samples before bulk purchasing to verify the material quality and suitability for your project.
10. Return Policies: Understand the supplier’s return policies for defective or unsuitable materials to safeguard your investment.
Sustainability
11. Eco-friendly Options: Consider suppliers that offer sustainable and eco-friendly materials if environmental impact is a concern.
By carefully considering these factors, you can ensure that your procurement process for CNC router projects is efficient, cost-effective, and aligned with your project goals.
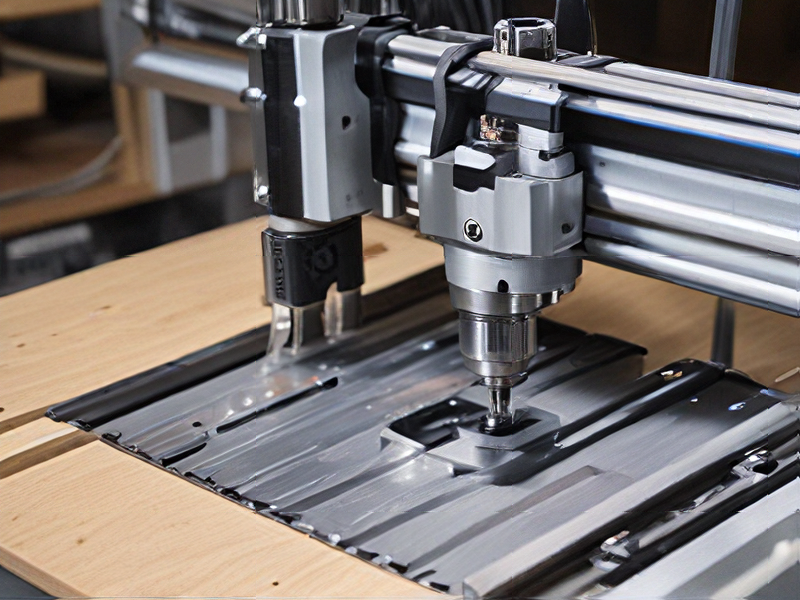

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from router cnc projects in China
Certainly! When sourcing and manufacturing CNC router projects in China, several frequently asked questions often arise:
1. What are the typical lead times for CNC router projects in China?
Lead times can vary based on project complexity and supplier capabilities. Generally, they range from a few weeks to several months, including production and shipping.
2. How do I ensure quality control during manufacturing?
Quality control is crucial. It’s essential to work closely with suppliers, conduct inspections at key production stages, and possibly hire third-party inspection services to maintain standards.
3. What are the main considerations for choosing a CNC router supplier in China?
Factors include experience with similar projects, production capacity, quality certifications, responsiveness to communication, and their ability to accommodate customization.
4. What are the payment terms typically expected?
Payment terms often involve an initial deposit (30-50%) with the balance due upon completion or before shipping. Negotiate terms that balance supplier needs with payment security.
5. How can intellectual property (IP) protection be ensured?
While IP protection is a concern, it’s advisable to have clear contracts, non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), and consider registering patents or designs in China if applicable.
6. What shipping options are available, and how do I handle customs?
Suppliers usually offer shipping via sea freight, air freight, or courier services like DHL. Handling customs involves proper documentation and possibly using a customs broker.
7. What are common challenges when manufacturing in China, and how can they be mitigated?
Challenges include language barriers, cultural differences, and potential delays. Mitigate these by clear communication, visiting suppliers if feasible, and building strong relationships.
Navigating these FAQs can help ensure smoother sourcing and manufacturing processes for CNC router projects in China, balancing cost-effectiveness with quality and reliability.