Technology and Applications of cnc lathe machining
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lathe machining is a technology where pre-programmed computer software dictates the movement of factory tools and machinery. This method is utilized to control a variety of complex machinery, from lathes and mills to routers and grinders. The process allows for precise, repeatable, and efficient production of parts and components.
Technology
CNC lathe machines operate on the principle of subtractive manufacturing, where material is removed from a workpiece to create the desired shape. The key components of a CNC lathe include:
1. Spindle: Holds and rotates the workpiece.
2. Cutting Tool: Mounted on a turret, it moves along multiple axes to shape the workpiece.
3. Control Unit: The computer that reads the design instructions (G-code) and translates them into machine movements.
CNC systems can produce highly complex and intricate parts with minimal human intervention, ensuring high precision and consistency. They incorporate various sensors and feedback systems to monitor and adjust operations in real-time, enhancing accuracy and reducing waste.
Applications
1. Automotive Industry: CNC lathes are used to produce parts such as engine components, gearboxes, and drive shafts, ensuring high precision and durability.
2. Aerospace: Critical components like turbine blades, landing gear parts, and structural elements are machined with exact specifications.
3. Medical Devices: Precision machining of surgical instruments, implants, and prosthetics demands the high accuracy provided by CNC lathes.
4. Electronics: Components such as connectors, housings, and semiconductor equipment benefit from the precision and efficiency of CNC machining.
5. Custom Manufacturing: CNC lathes enable the production of custom parts in small batches, catering to specialized needs across various industries.
CNC lathe machining represents a significant advancement in manufacturing technology, offering unparalleled precision, efficiency, and versatility across a broad spectrum of applications.
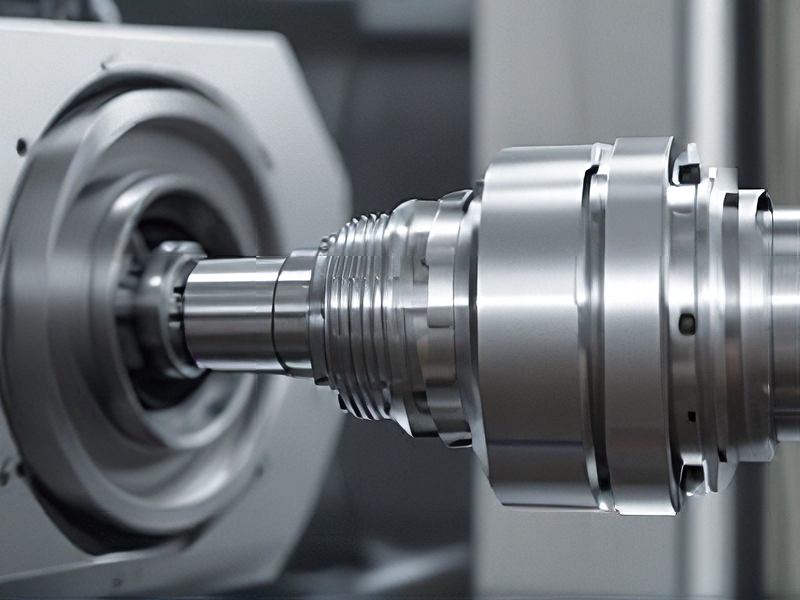
Quality Testing Methods for cnc lathe machining and how to control quality
Quality testing methods for CNC lathe machining typically involve both in-process and post-process inspections to ensure dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and overall part quality. Here are some common methods:
1. Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing precision measuring instruments such as calipers, micrometers, and gauges to verify critical dimensions specified in engineering drawings.
2. Surface Roughness Measurement: Assessing the surface finish using tools like profilometers to ensure it meets specified requirements.
3. Visual Inspection: Direct visual examination to detect surface defects, tool marks, burrs, and other imperfections that could affect functionality or aesthetics.
4. Tool Wear Monitoring: Regular checks on tool condition and wear using wear indicators or through automated monitoring systems integrated into the CNC machine.
5. First Article Inspection (FAI): Comprehensive inspection of the first produced part to verify that all specifications and requirements are met before proceeding with full production.
6. Statistical Process Control (SPC): Monitoring and controlling the machining process using statistical methods to ensure consistency and identify any variations that may affect quality.
To control quality effectively:
– Establish Clear Specifications: Define precise tolerances, surface finish requirements, and inspection criteria based on customer requirements and engineering standards.
– Regular Calibration: Ensure all measuring instruments and CNC machines are regularly calibrated to maintain accuracy.
– Operator Training: Provide comprehensive training to machine operators on quality standards, inspection methods, and the importance of adherence to specifications.
– Documentation and Traceability: Maintain detailed records of inspections, measurements, and any deviations encountered during the machining process for traceability and process improvement.
– Continuous Improvement: Implement feedback loops and corrective actions based on inspection results to prevent recurrence of defects and improve overall process capability.
By integrating these methods and controls into CNC lathe machining processes, manufacturers can consistently produce high-quality parts that meet customer expectations and industry standards.

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from cnc lathe machining
When procuring CNC lathe machining services, several key considerations and tips can help ensure a successful purchase:
1. Define Requirements Clearly:
– Precision and Tolerances: Specify the level of precision and tolerances required for your parts.
– Material Specifications: Detail the types of materials needed, considering their machinability and cost.
2. Supplier Evaluation:
– Experience and Expertise: Choose suppliers with proven expertise in CNC lathe machining and a strong track record.
– Certifications: Look for certifications like ISO 9001, which indicate quality management systems.
– Capacity and Capabilities: Ensure the supplier has the necessary machinery and capacity to meet your volume and complexity requirements.
3. Quality Assurance:
– Inspection Processes: Confirm that the supplier has robust inspection processes, including first-article inspection (FAI) and in-process checks.
– Quality Control Systems: Inquire about their quality control systems and how they handle non-conformance.
4. Cost Considerations:
– Cost Breakdown: Understand the cost structure, including setup fees, material costs, and per-unit machining costs.
– Value vs. Price: Balance cost with the quality and reliability of the supplier. The cheapest option may not always be the best.
5. Lead Times and Flexibility:
– Delivery Schedule: Verify lead times and ensure they align with your project timelines.
– Flexibility: Assess the supplier’s ability to accommodate changes in order volumes or design modifications.
6. Communication and Support:
– Technical Support: Ensure the supplier offers strong technical support and clear communication channels.
– Project Management: A supplier with dedicated project management can streamline the procurement process and address issues promptly.
7. Sample Production:
– Prototyping: Consider starting with a prototype to verify the supplier’s capabilities and the quality of the final product.
– Feedback Loop: Use the prototyping phase to provide feedback and make necessary adjustments.
8. Sustainability and Compliance:
– Environmental Practices: Check if the supplier follows sustainable manufacturing practices.
– Regulatory Compliance: Ensure compliance with relevant industry standards and regulations.
By meticulously evaluating these aspects, you can make informed decisions and establish a reliable partnership with your CNC lathe machining supplier.

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from cnc lathe machining in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from CNC Lathe Machining in China
1. Why should I consider CNC lathe machining in China?
– China offers cost-effective manufacturing solutions due to lower labor costs and advanced production capabilities. The country has a vast number of skilled workers and state-of-the-art technology, ensuring high-quality production.
2. How do I find reliable CNC lathe machining suppliers in China?
– Start with platforms like Alibaba, Global Sources, or Made-in-China. Verify suppliers through reviews, certifications, and by requesting samples. Visiting factories and trade shows can also help establish trust.
3. What are the benefits of CNC lathe machining?
– CNC lathe machining provides high precision, repeatability, and efficiency. It is suitable for producing complex parts with tight tolerances and ensures consistent quality across large production runs.
4. What materials can be used in CNC lathe machining?
– Common materials include metals (aluminum, steel, brass), plastics, and composites. The choice of material depends on the application and desired properties of the final product.
5. How can I ensure the quality of parts manufactured in China?
– Implement strict quality control measures, such as third-party inspections, in-process quality checks, and detailed contracts specifying standards and tolerances. Working with ISO-certified suppliers can also enhance quality assurance.
6. What is the typical lead time for CNC lathe machining in China?
– Lead times vary depending on the complexity and quantity of the order. Generally, it ranges from a few weeks to a couple of months. Discuss timelines with suppliers and ensure clear communication.
7. How do I handle logistics and shipping from China?
– Partner with experienced freight forwarders or logistics companies familiar with international shipping. They can assist with customs clearance, shipping options, and cost estimations.
8. What are the payment terms for CNC lathe machining in China?
– Common terms include a 30% deposit before production and 70% upon completion or before shipment. Letters of credit and escrow services are also used to secure transactions.
9. How do I deal with language and cultural barriers?
– Many Chinese suppliers have English-speaking staff. However, clear and concise communication, using simple language and visuals, can mitigate misunderstandings. Cultural sensitivity and patience are key.
10. What are the risks associated with CNC lathe machining in China?
– Potential risks include quality issues, intellectual property theft, and delays. Mitigate these risks by conducting thorough due diligence, establishing strong contracts, and maintaining regular communication with suppliers.

