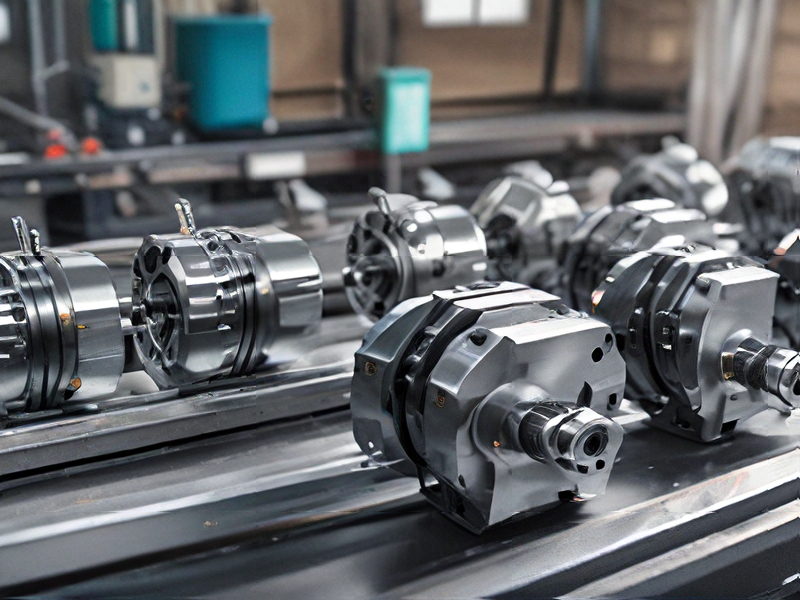
Technology and Applications of cnc and lathe machine
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) and lathe machines represent crucial advancements in manufacturing technology. CNC integrates computerized controls to automate machine tools, enhancing precision, speed, and efficiency in production processes. These machines operate through programmed instructions, converting digital designs into precise movements of cutting tools. They find extensive application across industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics for manufacturing complex components with high accuracy and consistency.
Lathe machines, a foundational tool in machining, shape workpieces by rotating them against cutting tools. Traditional lathes require manual operation, whereas CNC lathes automate processes, allowing for intricate designs and tighter tolerances. CNC lathe machines excel in turning operations—forming cylindrical components—enabling manufacturers to produce shafts, bolts, and bushings efficiently.
The synergy of CNC technology with lathe machines enhances manufacturing capabilities. CNC provides flexibility in producing varied geometries and materials, from metals to plastics, with minimal setup changes. Its integration with lathes facilitates multi-axis machining, live tooling for milling operations, and automated tool changes, optimizing production workflows and reducing human error.
Applications span from prototype development to mass production, catering to diverse industries’ demands for customized components. CNC lathe machines are pivotal in fabricating parts for medical implants, industrial pumps, and hydraulic systems, where precision and repeatability are critical.
In conclusion, CNC and lathe machines revolutionize manufacturing by combining advanced automation with traditional machining principles. Their synergy enables complex part production while enhancing productivity and quality across industrial sectors.

Quality Testing Methods for cnc and lathe machine and how to control quality
Quality Testing Methods for CNC and Lathe Machines
1. Dimensional Inspection:
– Tools: Micrometers, Vernier calipers, Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM).
– Purpose: Ensures parts meet specified dimensions and tolerances.
2. Surface Finish Inspection:
– Tools: Surface roughness testers.
– Purpose: Verifies the smoothness of the machined surface to meet the required finish.
3. Visual Inspection:
– Tools: Magnifying glasses, optical comparators.
– Purpose: Detects visible defects like burrs, scratches, or improper finishes.
4. Material Testing:
– Tools: Hardness testers, tensile testers, spectrometers.
– Purpose: Ensures material properties like hardness, tensile strength, and composition match specifications.
5. Functional Testing:
– Tools: Gauges, test rigs.
– Purpose: Verifies that parts function correctly in their intended applications.
6. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT):
– Methods: Ultrasonic testing, X-ray, dye penetrant inspection.
– Purpose: Detects internal defects without damaging the part.
Quality Control Measures
1. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs):
– Establish detailed procedures for each machining process.
– Ensure consistent execution by all operators.
2. Regular Calibration:
– Periodically calibrate all measuring instruments to maintain accuracy.
3. Statistical Process Control (SPC):
– Use control charts to monitor machining processes and detect variations.
– Implement corrective actions based on SPC data.
4. Operator Training:
– Provide continuous training to operators on the latest machining and quality control techniques.
5. Preventive Maintenance:
– Schedule regular maintenance of CNC and lathe machines to prevent unexpected breakdowns and ensure consistent performance.
6. Documentation and Traceability:
– Maintain detailed records of each part’s production history for traceability and accountability.
Implementing these methods and controls ensures high-quality outputs from CNC and lathe machining processes, meeting stringent industrial standards and customer expectations.
Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from cnc and lathe machine
When purchasing CNC (Computer Numerical Control) and lathe machines, several critical considerations can guide procurement decisions:
1. Machine Specifications: Understand the required specifications such as bed length, swing diameter (for lathes), spindle speed, tool changer capacity (for CNC machines), and tolerance levels needed for your projects.
2. Machine Accuracy and Repeatability: Check the machine’s accuracy ratings and repeatability to ensure they meet your production requirements.
3. Machine Rigidity and Stability: Evaluate the build quality, material, and rigidity of the machine to handle the intended workload and ensure long-term reliability.
4. Control System: Assess the CNC control system capabilities, user interface, and compatibility with your existing software and workflow.
5. Maintenance and Support: Inquire about the availability of spare parts, maintenance requirements, and the reputation of the manufacturer or supplier for after-sales support.
6. Training and Operator Skills: Consider the training required for operators to effectively use the machines and ensure compatibility with your team’s skill set.
7. Cost and ROI: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including initial purchase price, operational costs (such as energy consumption), and potential return on investment based on increased productivity or capability.
8. Supplier Reputation: Choose a reputable supplier with a history of delivering quality machinery and reliable customer service.
9. Future Expansion: Anticipate future needs and assess whether the machine can be upgraded or expanded to accommodate evolving production requirements.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision when purchasing CNC and lathe machines that aligns with your operational needs and business goals.

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from cnc and lathe machine in China
Certainly! When sourcing and manufacturing from CNC and lathe machine suppliers in China, it’s essential to address common concerns through the following FAQs:
1. How do I choose a reliable supplier?
– Research extensively online, check supplier directories, and request references. Ensure they have experience with international clients and certifications like ISO.
2. What are typical manufacturing lead times?
– Lead times vary based on complexity and volume but typically range from a few weeks to a couple of months. Discuss specific timelines with your supplier to align expectations.
3. Can I visit the factory before placing an order?
– Yes, it’s advisable to visit if feasible. This allows you to verify capabilities, quality control processes, and build a relationship with the supplier.
4. How can quality control be ensured?
– Specify quality standards in your contract and conduct inspections at key production stages. Third-party inspection services are also recommended.
5. What are the payment terms?
– Negotiate payment terms based on milestones or a deposit with balance upon completion. Avoid full payment upfront to mitigate risks.
6. What about intellectual property protection?
– Draft clear contracts addressing IP ownership and confidentiality. Consider legal advice and register patents or trademarks as necessary.
7. Are there regulatory considerations?
– Ensure compliance with local regulations for imports and exports, including tariffs, customs, and product certifications required in your market.
8. How do I handle shipping and logistics?
– Discuss shipping options (air, sea, courier) and responsibilities (FOB, CIF) with your supplier. Factor in transportation costs and insurance.
9. What if there are issues with the delivered goods?
– Have a clear process for handling defects or discrepancies. Promptly communicate concerns to the supplier and document all agreements in writing.
10. How do I communicate effectively with Chinese suppliers?
– Clearly outline expectations, specifications, and deadlines in writing. Consider using a reliable translator if language barriers exist.
By addressing these FAQs, you can navigate sourcing and manufacturing from CNC and lathe machine suppliers in China more effectively while minimizing potential risks and ensuring quality outcomes.

