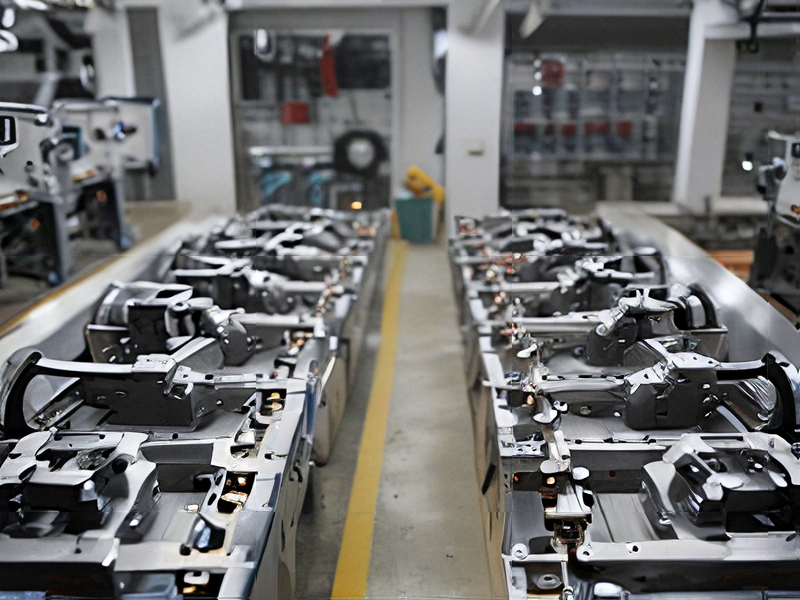
Technology and Applications of g code cnc programming
G-code (Geometric Code) is a programming language used in Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines to control their movements and operations. It consists of alphanumeric codes that instruct CNC machines on how to move, cut, and shape materials like metal, plastic, or wood.
Technology:
G-code commands are based on Cartesian coordinates (X, Y, Z axes) and include commands for tool movements (like G0 for rapid movement and G1 for linear interpolation), spindle speed (S command), feed rate (F command), and tool changes (M06 command). G-code files are typically generated by Computer-Aided Design (CAD) or Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software, which convert designs into machine-readable instructions.
Applications:
1. Manufacturing: CNC machines are used extensively in manufacturing industries for precision machining of components. They can create complex shapes with high accuracy and repeatability, making them ideal for industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
2. Prototyping: Rapid prototyping benefits from CNC machines as they can quickly produce prototypes based on CAD designs, allowing designers to test and refine their concepts before full-scale production.
3. Art and Sculpture: Artists and sculptors use CNC machines to create intricate artworks and sculptures that would be difficult or impossible to achieve manually.
4. Woodworking and Carpentry: CNC routers are used in woodworking to cut, carve, and shape wood precisely, enabling custom furniture and cabinetry production.
5. Education: CNC programming is taught in technical schools and universities to train students in manufacturing processes and automation.
6. Medical Industry: CNC machines are used to manufacture medical implants and devices with high precision and consistency.
G-code programming continues to evolve with advancements in CNC technology, incorporating features like multi-axis machining, adaptive toolpaths, and real-time feedback systems for enhanced productivity and efficiency in manufacturing processes.
Quality Testing Methods for g code cnc programming and how to control quality
Quality testing methods for CNC (Computer Numerical Control) programming in G-code typically involve several key approaches:
1. Simulation Software: Utilize specialized software to simulate the machining process based on the G-code. This helps identify potential errors in tool paths, collisions, or improper machining sequences before actual production.
2. Post-Processor Verification: Verify G-code output through post-processor simulation to ensure it correctly translates CAD/CAM instructions into machine-specific G-code commands.
3. Dry Runs: Conduct initial runs of the G-code on the CNC machine without material (dry runs) to check for unexpected movements, program errors, or tool path inaccuracies.
4. Measurement and Calibration: Regularly calibrate the CNC machine and measure machined parts against design specifications using precision measuring instruments to verify dimensional accuracy.
5. Documentation and Version Control: Maintain detailed documentation of G-code programs, revisions, and changes. Implement version control to track modifications and ensure consistency across production runs.
6. Peer Review and Testing: Have experienced programmers or quality assurance personnel review G-code programs for logic errors, safety concerns, and adherence to machining best practices.
To control quality effectively, establish clear processes for G-code development, testing, and validation. Implementing rigorous testing protocols and using simulation tools can significantly minimize errors and improve overall machining accuracy and efficiency. Regular training for programmers and operators also ensures adherence to quality standards and continuous improvement in CNC programming practices.
Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from g code cnc programming
When delving into procurement for G-code CNC programming, several key considerations ensure efficient purchasing:
1. Supplier Expertise: Opt for suppliers with expertise in CNC programming and G-code, ensuring they understand your specific needs and can provide tailored solutions.
2. Quality Assurance: Prioritize suppliers known for delivering high-quality G-code programs that meet industry standards and ensure precision in machining processes.
3. Compatibility: Ensure the G-code programs are compatible with your CNC machines and software. Compatibility issues can lead to inefficiencies and operational disruptions.
4. Customization: Depending on your requirements, assess whether suppliers can customize G-code programs to suit unique machining specifications or specific industry standards.
5. Cost and Value: Evaluate costs against the value delivered. Cheaper options might compromise on quality or support, impacting long-term operational efficiency.
6. Support and Maintenance: Choose suppliers who offer comprehensive support and maintenance services for G-code programs. This ensures prompt resolution of issues and minimal downtime.
7. Security: Consider the security of G-code files and intellectual property protection measures offered by suppliers to safeguard proprietary information.
8. Training and Documentation: Suppliers providing training on G-code programming and comprehensive documentation enhance user proficiency and troubleshooting capabilities.
9. Feedback and Reviews: Review supplier feedback and customer testimonials to gauge reliability, customer service, and overall satisfaction with their G-code programming services.
By considering these factors, procurement professionals can streamline the purchasing process for G-code CNC programming, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness in machining operations.
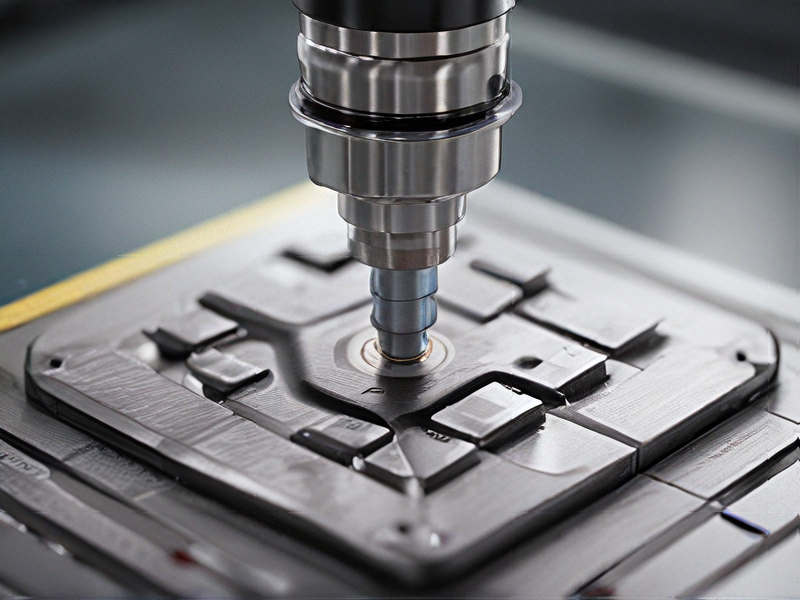

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from g code cnc programming in China
Certainly! Here are some FAQs on sourcing and manufacturing from G-code CNC programming in China:
1. What are the benefits of sourcing CNC manufacturing from China?
Sourcing from China often offers cost advantages due to lower labor and manufacturing costs. China also has a large base of skilled CNC programmers and operators.
2. How can I ensure quality when sourcing CNC services from China?
Quality assurance can be ensured through rigorous supplier selection, clear communication of specifications, regular inspections, and possibly visiting the manufacturing facilities.
3. Are there any language barriers when communicating CNC requirements?
Language barriers can exist, but many Chinese CNC manufacturers have English-speaking staff or employ translators. Clear and detailed documentation of requirements can also mitigate language issues.
4. What is the typical lead time for CNC manufacturing in China?
Lead times vary depending on complexity and volume but are generally competitive. Clear communication and planning can help manage expectations.
5. How do I protect my intellectual property (IP) when sourcing from China?
Protecting IP involves signing non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), conducting due diligence on suppliers, and potentially registering patents or trademarks in China.
6. Can Chinese CNC manufacturers handle custom G-code programming?
Yes, many Chinese CNC manufacturers are equipped to handle custom G-code programming to meet specific design and production requirements.
7. What are the payment terms typically used in China for CNC manufacturing?
Payment terms often include initial deposits and subsequent payments upon milestones or completion. Negotiating favorable terms is possible with clear contracts.
Navigating sourcing and manufacturing from G-code CNC programming in China involves understanding cultural differences, ensuring quality control measures, and protecting intellectual property while leveraging cost advantages.

