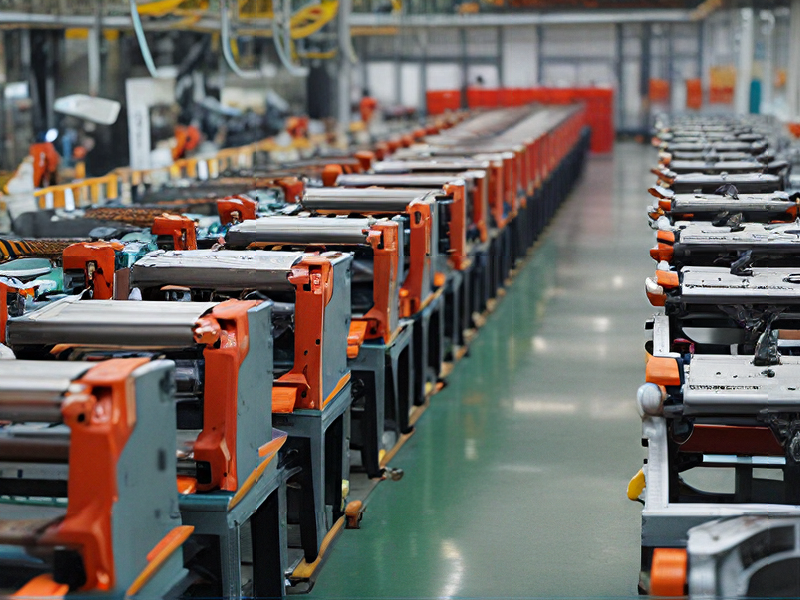
Technology and Applications of rapid manufacturing
Rapid manufacturing, often referred to as rapid prototyping or additive manufacturing, encompasses technologies that enable quick production of parts and prototypes directly from digital designs. Key technologies include:
1. Stereolithography (SLA): Uses a UV laser to solidify layers of photopolymer resin, building parts layer by layer.
2. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Utilizes a laser to sinter powdered materials (like nylon or metal) layer by layer, fusing them into solid objects.
3. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Melts and deposits thermoplastic filament through a heated nozzle to create layers based on a 3D model.
4. Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): Similar to SLS, but uses metal powders (like titanium or aluminum) to create fully dense metal parts.
Applications span various industries:
– Automotive: Prototyping of car parts for testing and design validation.
– Aerospace: Manufacturing lightweight components with complex geometries.
– Medical: Custom implants and prosthetics tailored to patient anatomy.
– Consumer Goods: Customized products and small batch production.
Benefits include rapid iteration, reduced time-to-market, and cost-effectiveness for low-volume production. Challenges include material limitations, post-processing requirements, and scalability for mass production. As technology advances, rapid manufacturing continues to evolve, offering new possibilities for innovation across industries.
Quality Testing Methods for rapid manufacturing and how to control quality
Rapid manufacturing requires robust quality testing methods to ensure product integrity and consistency. Key approaches include:
1. Computer-Aided Inspection (CAI): Utilizes CAD models to automate measurement and inspection processes, ensuring precise conformity to design specifications.
2. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like ultrasonic testing and X-ray inspection detect defects without damaging the product, crucial for maintaining structural integrity.
3. In-Line Monitoring: Real-time sensors and monitoring systems during manufacturing detect deviations promptly, allowing immediate corrective actions to maintain quality.
4. Statistical Process Control (SPC): Monitors production processes using statistical methods to ensure they operate within defined limits, reducing variability and defects.
5. Post-Processing Verification: Validates final product attributes against specifications through dimensional checks, surface analysis, and functional testing.
To control quality effectively:
1. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Establish clear protocols for each stage of manufacturing, ensuring consistency and adherence to quality standards.
2. Training and Skills Development: Equip personnel with training to operate machinery, perform inspections, and understand quality metrics.
3. Supplier Quality Management: Verify raw material and component quality from suppliers to maintain consistency in manufacturing inputs.
4. Continuous Improvement: Implement feedback loops from testing results to refine processes and enhance product quality iteratively.
5. Traceability and Documentation: Maintain comprehensive records of production steps and quality tests to trace issues and ensure accountability.
By integrating these methods and controls, manufacturers can achieve high-quality outputs in rapid manufacturing processes, meeting customer expectations and regulatory requirements efficiently.
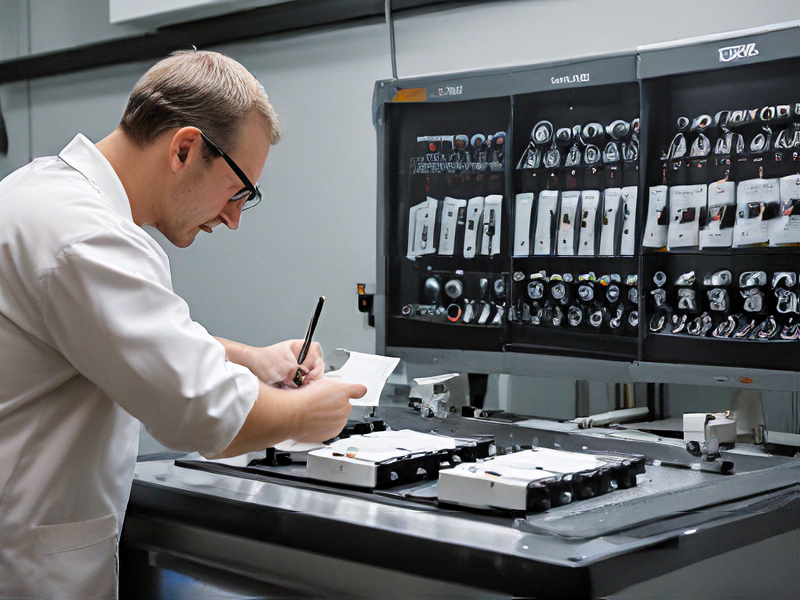

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from rapid manufacturing
Tips for Procurement from Rapid Manufacturing
1. Vendor Evaluation: Assess vendors based on their track record, customer reviews, and capability to meet your specific needs. Check for certifications and quality control processes.
2. Material Compatibility: Ensure the materials used in rapid manufacturing align with your product’s requirements, including strength, durability, and safety standards.
3. Technology Expertise: Choose a manufacturer with expertise in the technology you need, such as 3D printing, CNC machining, or injection molding. Their proficiency can significantly impact the quality and speed of production.
4. Prototyping and Testing: Utilize prototyping services to test the design and functionality of your product before committing to large-scale production. This step can save time and resources by identifying potential issues early.
5. Lead Times and Scalability: Confirm the vendor’s lead times and their ability to scale production quickly if needed. Rapid manufacturing is known for its speed, but capacity can vary.
6. Cost Transparency: Obtain detailed quotes that break down costs, including materials, labor, and any additional services. This transparency helps in budgeting and prevents unexpected expenses.
Considerations when Purchasing from Rapid Manufacturing
1. Quality Assurance: Ensure the manufacturer has robust quality assurance measures. This includes regular inspections and adherence to industry standards to maintain product consistency.
2. Intellectual Property (IP) Protection: Verify that the vendor has protocols to protect your IP. This is crucial when sharing designs and prototypes.
3. Environmental Impact: Consider the environmental policies of the manufacturer. Sustainable practices and materials can align with your company’s green initiatives.
4. Customization and Flexibility: Rapid manufacturing offers high customization. Confirm that the vendor can handle specific custom requirements and accommodate design changes efficiently.
5. Supply Chain Integration: Evaluate how well the vendor integrates into your existing supply chain. Effective communication and logistics coordination can minimize disruptions.
6. After-Sales Support: Assess the level of after-sales support offered. Reliable customer service can be invaluable for addressing post-production issues promptly.
These tips and considerations will help you make informed decisions, ensuring efficient, high-quality procurement from rapid manufacturing sources.

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from rapid manufacturing in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from Rapid Manufacturing in China
1. What is rapid manufacturing?
Rapid manufacturing involves using technologies like 3D printing, CNC machining, and injection molding to produce parts quickly and efficiently. It is ideal for prototypes and small to medium production runs.
2. Why choose China for rapid manufacturing?
China offers cost-effective manufacturing solutions due to its established supply chain, skilled workforce, and advanced technological capabilities. The country’s infrastructure supports high-speed production and delivery.
3. How can I ensure quality when sourcing from China?
To ensure quality, partner with reputable manufacturers, conduct factory audits, request samples, and implement strict quality control processes. Utilizing third-party inspection services can also help maintain standards.
4. What are the typical lead times for rapid manufacturing in China?
Lead times vary based on the complexity and volume of the order. Generally, prototypes can be produced within a few days to a week, while larger production runs might take several weeks.
5. How do I handle intellectual property (IP) protection?
To protect IP, use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), register patents, and work with manufacturers who have a track record of respecting IP rights. Legal counsel specializing in international trade can provide additional safeguards.
6. What are the costs involved in rapid manufacturing in China?
Costs depend on material, design complexity, quantity, and finishing requirements. China offers competitive pricing, but it’s crucial to consider shipping, tariffs, and potential hidden fees.
7. How do I choose the right manufacturing partner in China?
Research potential partners, evaluate their experience, technology, and certifications. Seek recommendations, visit facilities if possible, and start with smaller projects to assess reliability and quality.
8. What are the common challenges in sourcing from China?
Challenges include communication barriers, quality inconsistencies, longer lead times, and potential IP risks. Mitigating these involves thorough vetting of suppliers, clear contracts, and effective communication.
9. How is logistics managed for products manufactured in China?
Logistics can be managed through various shipping options like air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost savings. Collaborating with experienced logistics providers ensures smooth handling of customs and delivery.
10. Can rapid manufacturing in China handle customization?
Yes, Chinese manufacturers are highly adept at customization, allowing for tailored solutions to meet specific design and production needs.

