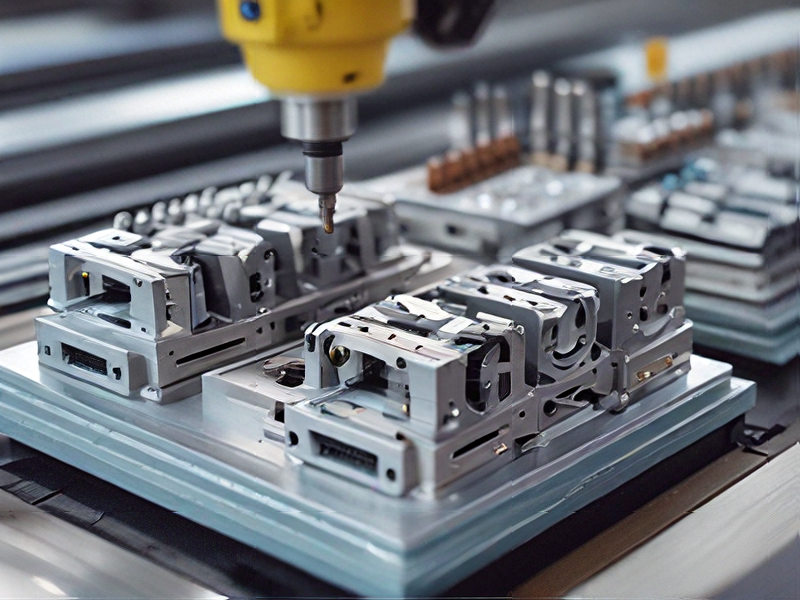
Technology and Applications of cnc machine desktop
Desktop CNC machines are compact, computer-controlled devices that bring industrial-level precision and capabilities to smaller scales. They utilize Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology to automate the cutting, milling, engraving, and drilling processes with high accuracy and repeatability. These machines are versatile, finding applications in various industries and hobbies due to their size and affordability.
In manufacturing, desktop CNC machines are used for rapid prototyping, small-scale production runs, and custom part manufacturing. They are particularly beneficial for producing intricate components with tight tolerances, such as circuit boards, jewelry, and small mechanical parts. Their ability to work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood, adds to their versatility.
In education and research, desktop CNC machines serve as valuable tools for teaching engineering principles, CNC programming, and manufacturing techniques in a hands-on manner. They allow students and researchers to experiment with different designs and iterate quickly, fostering creativity and innovation.
In the hobbyist and maker community, desktop CNC machines empower enthusiasts to turn their ideas into reality. Whether crafting personalized gifts, creating art installations, or building custom furniture, these machines enable hobbyists to explore their creativity without the space and cost requirements of larger industrial machines.
The technology behind desktop CNC machines continues to advance, with improvements in precision, ease of use through intuitive software interfaces, and connectivity options. As a result, they are becoming more accessible to a broader range of users, from professionals in need of rapid prototyping to hobbyists seeking to unleash their creativity.
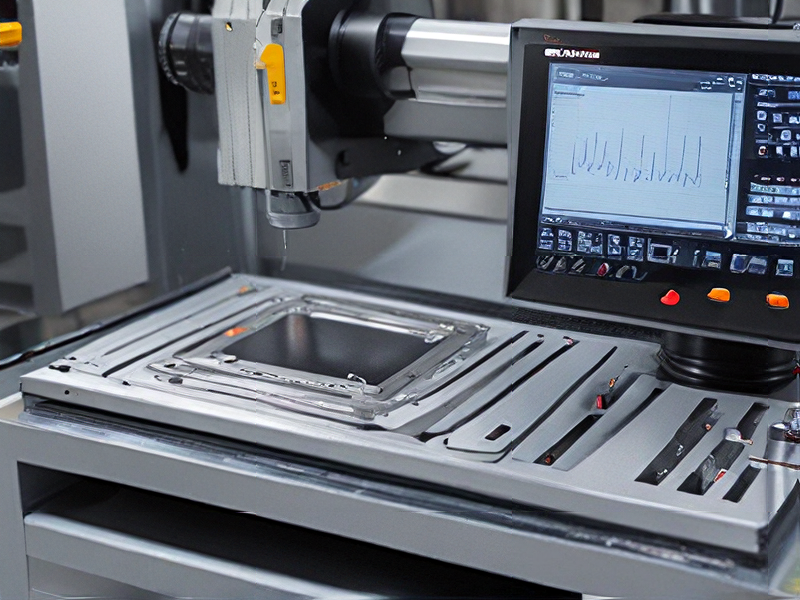

Quality Testing Methods for cnc machine desktop and how to control quality
Quality testing methods for CNC desktop machines and their control include:
1. Dimensional Accuracy Tests: Use precision measuring tools like calipers, micrometers, and CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines) to check if the produced parts meet the specified dimensions and tolerances.
2. Surface Finish Inspection: Employ surface roughness testers or profilometers to measure the surface finish of machined parts, ensuring they meet the required specifications.
3. Material Hardness Testing: Conduct hardness tests (e.g., Rockwell, Vickers) to ensure the material properties are consistent and within the desired range.
4. Alignment and Calibration Checks: Regularly calibrate the machine using laser interferometers or ballbar systems to ensure the machine’s axes are correctly aligned and movements are precise.
5. Tool Wear Monitoring: Use tool condition monitoring systems to detect tool wear and prevent it from affecting part quality. Implement regular tool change schedules based on tool life data.
6. Thermal Stability Tests: Measure the machine’s thermal stability using thermal imaging cameras or temperature sensors to ensure thermal growth does not impact precision.
7. Vibration Analysis: Conduct vibration analysis to detect any abnormal vibrations that could indicate machine wear or malfunction.
Quality Control Practices:
1. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop and follow detailed SOPs for machine setup, operation, and maintenance.
2. Regular Maintenance: Implement a preventive maintenance schedule to keep the machine in optimal condition.
3. Operator Training: Ensure operators are well-trained in machine operation, troubleshooting, and quality inspection techniques.
4. Statistical Process Control (SPC): Use SPC tools to monitor production processes and identify any deviations from the desired quality standards.
5. Documentation and Traceability: Maintain thorough documentation of all quality checks, machine calibrations, and maintenance activities to ensure traceability and accountability.
By integrating these testing methods and control practices, quality in CNC machining can be effectively maintained and improved.
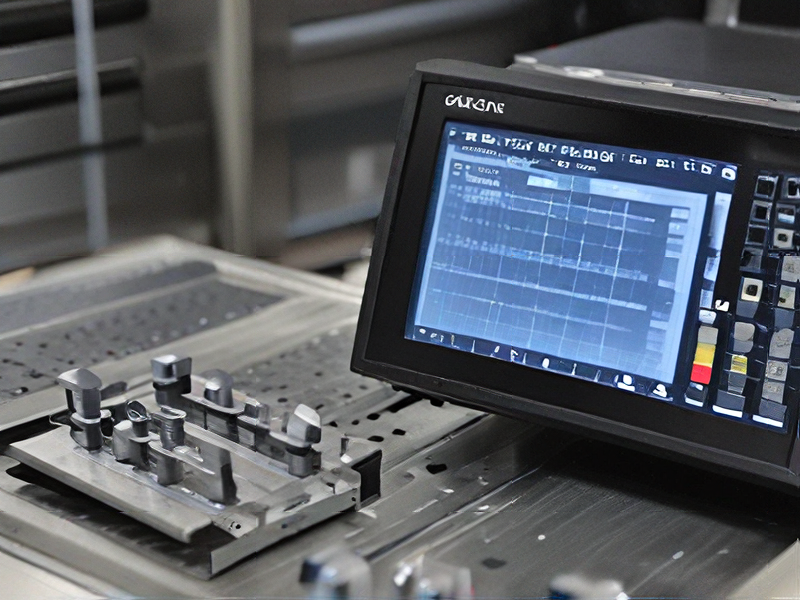

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from cnc machine desktop
When procuring a desktop CNC machine, several factors need careful consideration to ensure you select the right machine for your needs. Here are some essential tips and considerations:
1. Define Your Needs
– Purpose: Understand the primary purpose of the machine. Are you using it for hobby projects, small-scale production, or educational purposes?
– Material: Determine the types of materials you will be working with (e.g., wood, metal, plastic).
2. Specifications
– Work Area: Ensure the machine’s working area is suitable for the size of your projects.
– Spindle Power: Choose a spindle with sufficient power for your material and project needs.
– Accuracy and Precision: Check the machine’s precision specifications, especially if you require high accuracy.
3. Software Compatibility
– CAD/CAM Software: Verify that the CNC machine is compatible with your preferred CAD/CAM software.
– Ease of Use: Consider the learning curve of the software provided or required.
4. Quality and Durability
– Build Quality: Look for machines with robust construction for longevity and stability.
– Brand Reputation: Research the manufacturer’s reputation for quality and customer support.
5. Budget
– Initial Cost: Ensure the machine fits within your budget without compromising essential features.
– Maintenance and Upgrades: Factor in the cost of maintenance, potential upgrades, and consumables.
6. Customer Support and Warranty
– Support: Choose a vendor with reliable customer support.
– Warranty: Check the warranty terms and conditions for the machine.
7. Community and Resources
– User Community: A strong user community can provide valuable support and insights.
– Training Resources: Availability of tutorials, forums, and user guides can ease the learning process.
8. Safety Features
– Safety Protocols: Ensure the machine has adequate safety features to prevent accidents.
– Emergency Stops: Look for features like emergency stop buttons and safety enclosures.
By thoroughly evaluating these factors, you can make a well-informed decision and select a desktop CNC machine that meets your requirements and enhances your productivity.

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from cnc machine desktop in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing CNC Machine Desktops from China
1. Why source CNC machine desktops from China?
China offers competitive pricing, advanced manufacturing technology, and a vast selection of suppliers. This combination allows for cost-effective production without sacrificing quality.
2. How do I find reliable CNC machine desktop manufacturers in China?
Use platforms like Alibaba, Made-in-China, and Global Sources to find verified suppliers. Additionally, attending trade shows and seeking recommendations can help identify reputable manufacturers.
3. What factors should I consider when selecting a manufacturer?
Evaluate the manufacturer’s experience, certifications, production capacity, quality control processes, and customer reviews. Requesting samples and visiting the factory, if possible, are also recommended.
4. What are the common payment terms?
Typical payment terms include a 30% deposit before production and the remaining 70% upon shipment. Payment methods often accepted are bank transfers (T/T), letters of credit (L/C), and sometimes PayPal for smaller transactions.
5. How can I ensure the quality of the CNC machine desktops?
Implement strict quality control measures, such as requesting detailed product specifications, conducting factory audits, and using third-party inspection services to check the products before shipment.
6. What are the shipping options and costs?
Shipping can be done via sea freight, air freight, or express courier services. Sea freight is cost-effective for large orders, while air freight is faster but more expensive. Costs depend on the shipment size, weight, and destination.
7. How do I handle customs and import duties?
Hire a freight forwarder or customs broker to navigate customs regulations and duties. They can assist with documentation, tariff classifications, and ensuring compliance with import laws.
8. Are there any risks involved in sourcing from China?
Risks include potential quality issues, communication barriers, intellectual property theft, and logistical challenges. Mitigate these risks by conducting thorough due diligence, maintaining clear communication, and securing contracts.
9. What is the typical lead time for manufacturing?
Lead times vary depending on the manufacturer’s schedule and order complexity but generally range from 30 to 60 days.
By understanding these key aspects, you can effectively manage the sourcing and manufacturing process for CNC machine desktops from China.