Technology and Applications of etching of metals
Metal etching is a versatile technology used in various applications across industries. It involves selectively removing metal to create intricate patterns or shapes on the surface using chemical, electrochemical, or physical methods.
In electronics, metal etching is crucial for manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs). By selectively etching away copper layers deposited on substrates, PCBs are created with intricate circuit patterns that enable electronic devices to function. This process ensures precision and reliability in electrical connections.
In the automotive industry, metal etching plays a role in manufacturing components like fuel injector nozzles and gears. By etching metal surfaces, manufacturers achieve precise tolerances and surface finishes that enhance performance and durability of automotive parts.
Artistic and decorative applications also benefit from metal etching. Artists use etching techniques to create detailed designs on metal plates for printmaking, resulting in unique artworks with fine details and textures. Jewelry makers employ metal etching to add intricate patterns and textures to pieces, enhancing their aesthetic appeal.
In microfabrication and MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems), metal etching enables the creation of miniaturized components and sensors. By etching metal layers with high precision, engineers achieve precise geometries necessary for microelectronics and sensor technologies.
Overall, metal etching is a fundamental process in modern manufacturing and fabrication, enabling the production of intricate designs, functional components, and electronic devices across various industries. Its versatility and precision make it indispensable in both industrial applications and artistic endeavors.
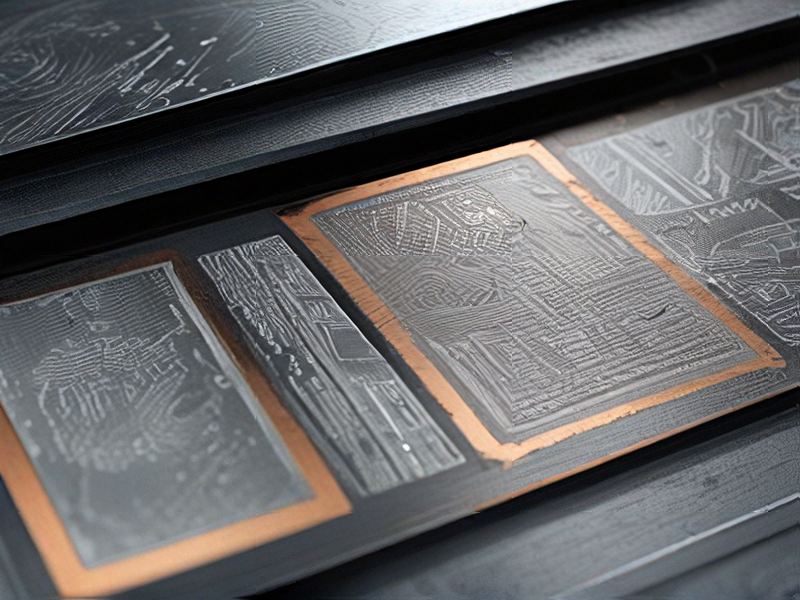

Quality Testing Methods for etching of metals and how to control quality
Quality Testing Methods for Etching of Metals
1. Visual Inspection:
– Purpose: Identifies surface defects, uneven etching, and residual contaminants.
– Method: Use magnifying lenses or microscopes to detect imperfections.
2. Microscopic Analysis:
– Purpose: Examines microstructural changes and uniformity of the etched patterns.
– Method: Employ optical or electron microscopes to assess fine details.
3. Profilometry:
– Purpose: Measures the depth and profile of etched features.
– Method: Utilize contact or non-contact profilometers to quantify etching depth and surface roughness.
4. X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF):
– Purpose: Analyzes the composition of the etched surface.
– Method: XRF spectrometers detect elemental composition to ensure the correct material is etched.
5. Adhesion Testing:
– Purpose: Assesses the bonding quality of subsequent layers applied after etching.
– Method: Use tape tests or pull-off tests to evaluate adhesion strength.
6. Chemical Analysis:
– Purpose: Detects residual etching agents or contaminants.
– Method: Techniques like titration or spectroscopy analyze chemical residues.
7. Dimensional Analysis:
– Purpose: Ensures the etched dimensions meet specifications.
– Method: Use calipers, micrometers, or coordinate measuring machines (CMM).
Controlling Quality
1. Process Standardization:
– Develop and follow standardized procedures for etching, including time, temperature, and chemical concentrations.
2. Regular Calibration:
– Ensure all measuring instruments and equipment are regularly calibrated for accuracy.
3. Environmental Control:
– Maintain controlled environments to prevent contamination and ensure consistent etching conditions.
4. Training and Certification:
– Train personnel in etching techniques and quality control measures, certifying them for specific tasks.
5. Batch Testing:
– Implement batch testing to regularly check for consistency and quality of etching processes.
6. Feedback Loops:
– Establish feedback mechanisms to quickly address defects or process deviations.
These methods and controls help maintain high standards in metal etching, ensuring reliability and performance of the final products.
Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from etching of metals
When procuring etched metal products, several key considerations can ensure quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some tips and considerations for purchasing etched metals:
Tips for Procurement
1. Specify Requirements Clearly: Clearly outline the specifications, including material type, thickness, dimensions, and tolerances. Provide detailed drawings and etching patterns to avoid miscommunication.
2. Supplier Selection: Choose suppliers with a proven track record in etching metals. Assess their experience, production capabilities, quality control processes, and customer reviews.
3. Material Quality: Ensure the supplier uses high-quality raw materials. The choice of metal (such as stainless steel, copper, or brass) should match the intended application to ensure durability and performance.
4. Sample and Prototyping: Request samples or prototypes to evaluate the quality of the etching and adherence to specifications before placing a larger order.
5. Quality Control: Verify the supplier’s quality control measures. Regular inspections and adherence to industry standards (such as ISO certifications) are critical for ensuring consistent quality.
Considerations When Purchasing
1. Design Complexity: Consider the complexity of your design. Intricate patterns may require advanced etching techniques and could affect lead times and costs.
2. Production Volume: Determine the required volume. High-volume orders may benefit from bulk pricing but ensure the supplier can scale production without compromising quality.
3. Lead Time: Account for production and shipping lead times. Ensure the supplier can meet your deadlines, especially if the etched metals are critical components in your production process.
4. Cost Factors: Evaluate the total cost, including material costs, etching fees, tooling costs (if applicable), and shipping. Request detailed quotes to compare and negotiate effectively.
5. Environmental and Safety Standards: Ensure the supplier complies with environmental regulations and safety standards. Eco-friendly etching processes and proper waste disposal are important considerations.
By focusing on these tips and considerations, you can streamline the procurement process, ensure high-quality etched metal products, and achieve cost savings and efficiency.

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from etching of metals in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing Etched Metals in China
1. Why source etched metals from China?
China offers competitive pricing, advanced manufacturing technologies, and a vast selection of suppliers with expertise in etching various metals. This makes it an attractive option for businesses looking to minimize costs while ensuring high-quality products.
2. What metals can be etched in China?
Common metals include stainless steel, copper, brass, aluminum, and nickel. Specialized suppliers can also handle other metals and alloys based on your specific needs.
3. What etching techniques are used?
Chemical etching is the most common method, but laser etching and photochemical machining are also widely available. The choice of technique depends on the material and the desired precision.
4. How do I find reliable suppliers?
Utilize online platforms like Alibaba, Made-in-China, or Global Sources. Look for suppliers with verified certifications, positive reviews, and robust quality control processes. Visiting trade shows or hiring sourcing agents can also help identify reputable manufacturers.
5. What are the typical lead times?
Lead times vary based on the complexity and volume of the order. Generally, prototypes take 2-3 weeks, while full production runs may require 4-8 weeks.
6. How can I ensure quality?
Request samples before full production, conduct factory audits, and insist on detailed quality control reports. Engaging third-party inspection services can also help maintain quality standards.
7. What are the common costs involved?
Costs include the price of raw materials, etching process fees, tooling costs (if any), shipping, and customs duties. Request detailed quotations to understand all cost components.
8. What are the shipping options?
Shipping can be done via sea or air, depending on urgency and budget. Sea freight is cost-effective for large orders, while air freight is faster but more expensive.
9. Are there any risks?
Common risks include communication barriers, quality inconsistencies, and intellectual property concerns. Mitigate these by establishing clear contracts, protecting IP rights, and maintaining regular communication.
10. What about sustainability and environmental regulations?
Many Chinese manufacturers adhere to international environmental standards, but it’s essential to verify their compliance with specific regulations to ensure sustainable practices.
By considering these FAQs, businesses can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing and manufacturing etched metals in China.

