Technology and Applications of laser engraving metal machine
Laser engraving metal machines use focused laser beams to etch precise and intricate designs onto various metal surfaces. This technology leverages high-powered lasers, such as fiber, CO2, or Nd:YAG, to vaporize the surface material, creating permanent markings.
Technology:
1. Laser Source: Fiber lasers are preferred for metal engraving due to their high efficiency and precision. They use optical fibers doped with rare-earth elements, emitting concentrated laser beams.
2. Galvanometer Systems: These mirror systems direct the laser beam across the metal surface, enabling high-speed engraving with fine detail.
3. Cooling Systems: To prevent overheating, laser machines use air or water cooling systems, ensuring stable operation and prolonging machine life.
4. Software: Advanced software controls the laser parameters, including speed, power, and frequency, allowing for customization and automation of the engraving process.
Applications:
1. Industrial Marking: Used for serial numbers, barcodes, and logos on products for traceability and branding in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
2. Jewelry and Personalization: Ideal for customizing jewelry, watches, and gifts with intricate designs and text, adding value through personalization.
3. Tool and Die Making: Engraves precise measurements and markings on tools and dies, ensuring accuracy in manufacturing processes.
4. Medical Devices: Marks surgical instruments and medical devices with critical information like batch numbers and expiration dates, complying with regulatory standards.
5. Art and Decoration: Creates detailed artistic designs on metal surfaces, used in decorative items and art pieces.
Laser engraving metal machines are valued for their precision, durability, and versatility, making them essential in various sectors requiring detailed and permanent metal markings.
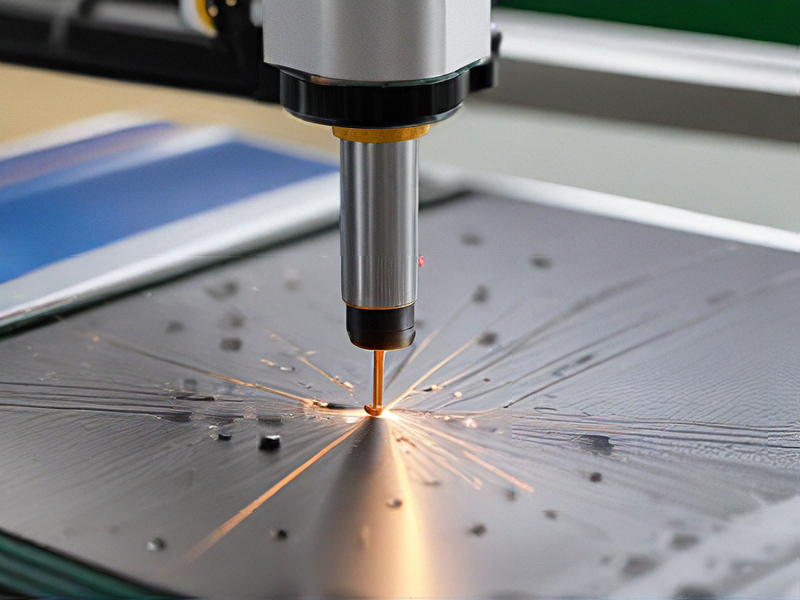
Quality Testing Methods for laser engraving metal machine and how to control quality
Quality Testing Methods for Laser Engraving Metal Machines
1. Visual Inspection:
– Objective: Check for surface defects, engraving accuracy, and clarity.
– Method: Inspect the engraved metal under adequate lighting, often using magnification tools to detect fine details and imperfections.
2. Dimensional Accuracy:
– Objective: Ensure that the engraving matches the specified dimensions and tolerances.
– Method: Use calipers, micrometers, or laser measurement tools to compare the engraved dimensions with the design specifications.
3. Surface Roughness Testing:
– Objective: Measure the smoothness of the engraved surface.
– Method: Employ a profilometer to quantify the surface roughness, ensuring it meets the required standards for the specific application.
4. Depth Measurement:
– Objective: Verify the depth of the engraving.
– Method: Utilize depth gauges or microscopes equipped with measurement software to accurately measure the depth.
5. Adhesion Testing:
– Objective: Assess the bonding strength of any coatings or films used in the engraving process.
– Method: Perform tape tests or cross-hatch tests to evaluate the adhesion quality.
6. Microstructure Analysis:
– Objective: Examine the microscopic structure of the engraved area.
– Method: Use scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to inspect the microstructural integrity of the material.
Quality Control Methods
1. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs):
– Develop and enforce detailed SOPs for the laser engraving process to ensure consistency.
2. Calibration and Maintenance:
– Regularly calibrate laser engraving machines and maintain them to avoid deviations and machine wear affecting quality.
3. Process Monitoring:
– Continuously monitor key parameters like laser power, speed, and focus. Use real-time data to make adjustments as needed.
4. Training and Certification:
– Ensure operators are well-trained and certified, emphasizing the importance of adherence to quality standards and procedures.
5. Batch Testing:
– Perform quality tests on sample batches from each production run to identify and address any deviations promptly.
6. Feedback Loops:
– Implement a system for collecting and analyzing feedback from customers and internal audits to drive continuous improvement.
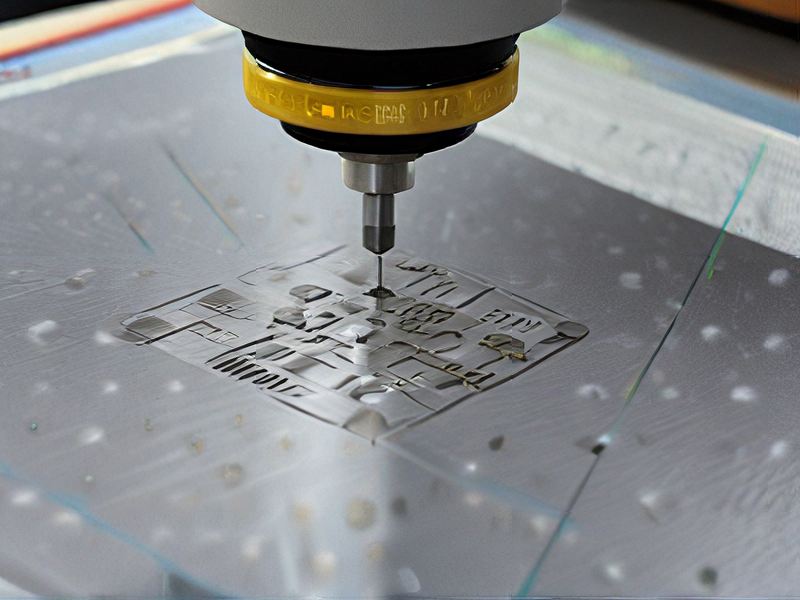
Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from laser engraving metal machine
When purchasing a laser engraving metal machine, several tips and considerations can ensure you make a well-informed decision:
1. Understand Your Needs:
– Determine the primary materials you’ll be engraving (e.g., aluminum, stainless steel, brass).
– Identify the specific applications, such as marking, engraving, or cutting.
2. Technical Specifications:
– Power Output: Higher wattage provides deeper and faster engraving.
– Laser Type: Fiber lasers are typically preferred for metal due to their efficiency and precision.
– Bed Size: Ensure the machine’s working area matches the size of the items you’ll be engraving.
– Cooling System: Effective cooling systems, like water or air cooling, extend machine life and maintain performance.
3. Software Compatibility:
– Check if the machine comes with user-friendly software compatible with your operating system.
– Ensure the software supports the file formats you commonly use (e.g., AI, DXF, PLT).
4. Precision and Speed:
– Look for machines that offer high precision (small spot size) and speed to meet your production needs.
5. Durability and Build Quality:
– Opt for machines built with robust materials to withstand industrial use.
6. Support and Warranty:
– Verify the availability of technical support and training.
– Look for machines with comprehensive warranties, covering critical components like the laser source and control systems.
7. Cost and ROI:
– Consider the machine’s total cost of ownership, including maintenance, consumables, and operational costs.
– Evaluate the potential return on investment by estimating productivity gains and quality improvements.
8. Safety Features:
– Ensure the machine includes necessary safety features, such as enclosed work areas, fume extractors, and safety interlocks.
By thoroughly evaluating these factors, you can choose a laser engraving metal machine that aligns with your operational needs and budget, ensuring long-term satisfaction and productivity.

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from laser engraving metal machine in China
Certainly! Here are some FAQs regarding sourcing and manufacturing from laser engraving metal machines in China:
1. What types of laser engraving machines are available in China?
Chinese manufacturers offer a wide range of laser engraving machines suitable for various materials and applications. Common types include CO2, fiber, and diode lasers.
2. How do I choose a reliable supplier in China?
Research is crucial. Look for suppliers with a proven track record, positive customer reviews, certifications (like ISO), and clear communication in English.
3. What are the typical costs involved?
Costs vary based on machine type, power, and additional features. Generally, prices range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars. Be wary of unusually low prices, as they may indicate quality issues.
4. Can I visit the manufacturer before purchasing?
Yes, many manufacturers welcome visits. It’s advisable to inspect production facilities, meet the team, and clarify any concerns about quality and manufacturing processes.
5. What about quality control and after-sales support?
Ensure the supplier has robust quality control measures in place. Ask about warranty terms, technical support availability, and spare parts accessibility to support ongoing operation and maintenance.
6. Are there any import regulations or duties to consider?
Import regulations vary by country. Research applicable tariffs, customs procedures, and any certifications needed for importing laser equipment.
7. What should I consider regarding shipping and logistics?
Discuss shipping options with your supplier. Consider factors like shipping times, insurance, and potential customs clearance delays.
8. How can I ensure intellectual property protection?
Sign clear contracts that include clauses on intellectual property rights. Consider legal advice and register patents or trademarks where necessary.
9. What are common challenges when sourcing from China?
Challenges may include language barriers, cultural differences, and potential delays. Effective communication and thorough due diligence can mitigate these issues.
10. How do I handle disputes or quality issues?
Establish clear communication channels and document agreements. Work collaboratively with the supplier to resolve issues promptly, leveraging any warranties or guarantees provided.
Navigating sourcing and manufacturing from China requires careful planning and due diligence to ensure a successful partnership and quality products.

