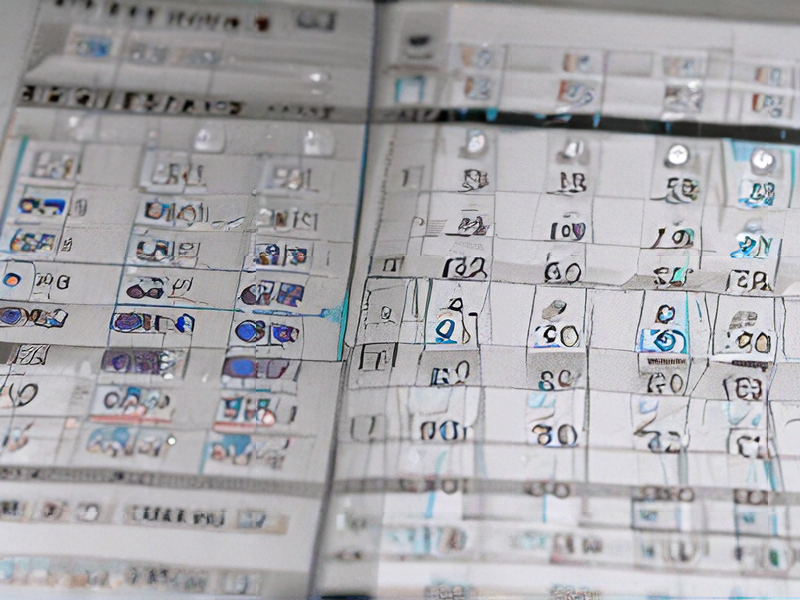
Technology and Applications of machining finish chart
Technology and Applications of Machining Finish Chart
Machining finish charts are essential tools in manufacturing, helping engineers and machinists determine the appropriate surface finish for different applications. Surface finish, often measured in microinches or micrometers, directly impacts the performance, functionality, and aesthetics of machined parts. Here are key points about the technology and applications:
#### Technology
1. Measurement Techniques: Surface finish is measured using profilometers (contact and non-contact), optical interferometers, and surface roughness testers. These instruments provide precise readings of surface irregularities.
2. Surface Finish Symbols: The chart includes various symbols and values, such as Ra (average roughness), Rz (average maximum height), and Rt (total height of the profile). These parameters quantify surface texture, influencing factors like friction, wear, and lubrication.
3. Machining Processes:
– Turning and Milling: Commonly achieve finishes in the range of 32-125 microinches (Ra).
– Grinding and Honing: Provide finer finishes, typically between 8-16 microinches (Ra).
– Polishing and Lapping: Attain ultra-fine finishes, often below 1 microinch (Ra).
#### Applications
1. Aerospace: Requires high-precision finishes to ensure aerodynamic efficiency and component longevity. Turbine blades and engine components often undergo fine grinding and polishing.
2. Automotive: Engine parts, such as cylinders and crankshafts, demand specific surface finishes for optimal performance and reduced wear. Honing is frequently used to achieve these finishes.
3. Medical Devices: Implants and surgical instruments require ultra-smooth surfaces to prevent bacterial growth and ensure biocompatibility. Polishing and lapping are crucial in this field.
4. Tool and Die Making: Dies and molds used in manufacturing processes need precise surface finishes to produce high-quality products. Grinding and EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) are common methods.
Machining finish charts guide the selection of finishing processes to meet the stringent requirements of various industries, ensuring functionality, durability, and quality of machined parts.
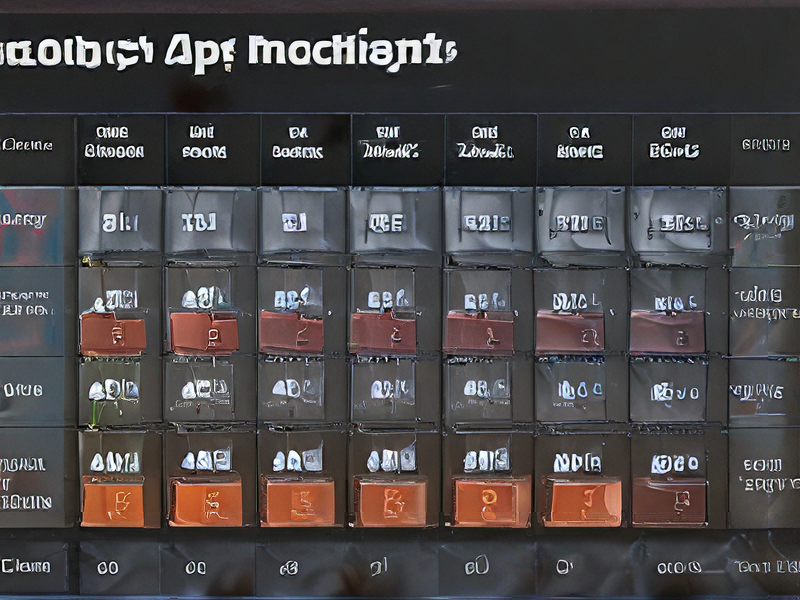
Quality Testing Methods for machining finish chart and how to control quality
To ensure machining finish quality, several methods can be employed along with effective quality control measures:
1. Surface Roughness Measurement: Utilize instruments like profilometers to quantify the roughness average (Ra) or root mean square (RMS) of machined surfaces against specified tolerances.
2. Visual Inspection: Conduct visual checks to detect defects such as scratches, pits, or uneven surfaces that might affect the finish.
3. Dimensional Inspection: Verify critical dimensions using calibrated tools like micrometers or calipers to ensure adherence to design specifications.
4. Comparative Analysis: Compare finished parts with standard samples or digital models using coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to ensure dimensional accuracy and surface finish consistency.
5. Process Parameters Control: Monitor and adjust machining parameters (e.g., cutting speed, feed rate, tool wear) to optimize surface finish and maintain consistency.
6. Statistical Process Control (SPC): Implement SPC techniques to monitor process stability and capability, ensuring variations in surface finish are within acceptable limits.
7. Feedback and Improvement: Establish feedback loops to address quality issues promptly, incorporating continuous improvement practices to refine machining processes.
By integrating these methods, manufacturers can achieve and maintain high-quality machining finishes, meeting customer expectations and ensuring consistent product performance.
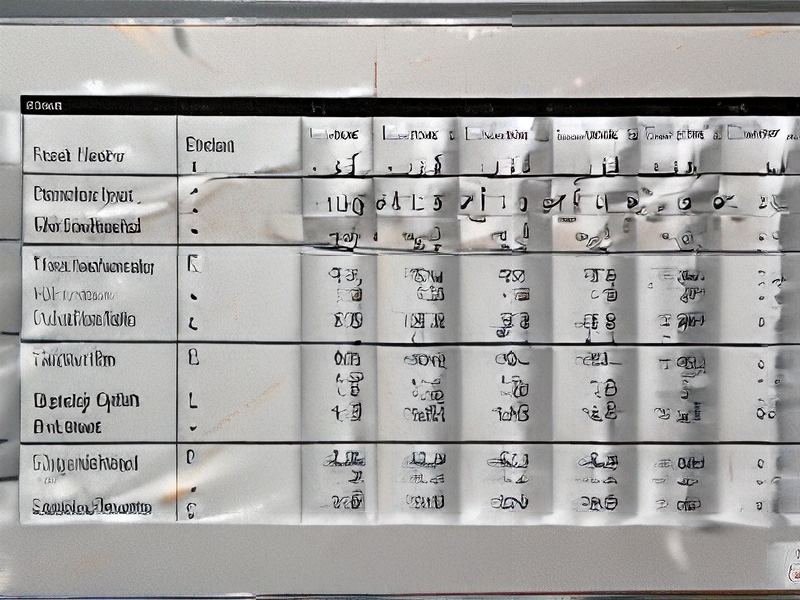
Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from machining finish chart
When procuring machined parts, a machining finish chart is crucial. Here are some tips and considerations:
Tips for Procurement:
1. Specify Requirements Clearly:
– Ensure that the required surface finish (Ra, Rz, etc.) is clearly stated on the drawings or procurement documents.
2. Select Appropriate Materials:
– Different materials have varying capabilities in achieving certain finishes. Choose materials that can meet your surface finish requirements without excessive processing.
3. Understand Machining Capabilities:
– Not all machining processes can achieve the same surface finish. Understand the capabilities of turning, milling, grinding, and other processes.
4. Supplier Qualifications:
– Verify that suppliers have the necessary equipment and expertise to achieve the specified surface finishes.
5. Quality Control:
– Ensure suppliers have robust quality control measures to verify surface finish, such as profilometers or visual inspections.
Considerations:
1. Cost Implications:
– Finer surface finishes often require more precise and slower machining processes, increasing cost. Balance surface finish requirements with budget constraints.
2. Functionality and Performance:
– Determine the necessity of the specified surface finish. Some applications require a high finish for performance, while others may not.
3. Tolerances:
– Surface finish can affect part dimensions. Ensure that surface finish requirements align with dimensional tolerances.
4. Post-Processing:
– Consider if post-processing like polishing or coating is needed to achieve the desired finish and how it impacts cost and lead time.
5. Lead Time:
– Achieving certain surface finishes can increase manufacturing time. Factor this into your project timelines.
6. Environmental Conditions:
– Surface finish can influence how parts behave in different environments, such as corrosion resistance. Match finishes to environmental conditions.
By addressing these tips and considerations, you can make informed decisions and procure machined parts that meet your quality, cost, and functional requirements efficiently.

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from machining finish chart in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from Machining Finish Chart in China
#### 1. What is a machining finish chart?
A machining finish chart provides a standard for surface finish quality in manufacturing, indicating the roughness and texture of machined parts.
#### 2. Why source from China?
China offers competitive pricing, a vast network of suppliers, and advanced manufacturing capabilities. The country also has significant experience in producing high-quality machined parts.
#### 3. How to select a reliable supplier?
– Research: Look for suppliers with positive reviews and ratings.
– Certifications: Ensure they have relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001).
– Samples: Request samples to assess quality.
– Audits: Conduct factory audits if possible.
#### 4. What are common surface finishes available in China?
Chinese manufacturers offer various surface finishes such as:
– Ra (Roughness Average): Commonly used metric.
– N (Nomenclature): Defines different surface quality levels (N1 to N12).
– Specific Textures: Mirror finish, matte, brushed, etc.
#### 5. What are typical lead times?
Lead times can vary but generally range from 2 to 8 weeks, depending on complexity, quantity, and customization requirements.
#### 6. How are quality control and inspection managed?
– In-house QC: Many factories have dedicated quality control teams.
– Third-Party Inspection: Hiring independent inspection agencies.
– Standards Compliance: Adhering to international quality standards.
#### 7. What are the payment terms?
Common terms include:
– TT (Telegraphic Transfer): Typically 30% upfront, 70% before shipment.
– LC (Letter of Credit): Ensures safer transactions for both parties.
#### 8. What about shipping and logistics?
– Modes: Air, sea, or land depending on urgency and cost.
– Incoterms: Familiarize yourself with Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) for clarity on responsibilities.
#### 9. How to handle communication barriers?
– Language: Use bilingual representatives or translators.
– Tools: Utilize communication tools like email, WeChat, and video calls.
#### 10. What are the risks and how to mitigate them?
– Risk: Delays, quality issues.
– Mitigation: Clear contracts, regular updates, and contingency plans.
By understanding these aspects, you can effectively source and manage manufacturing from machining finish charts in China.