Technology and Applications of metal injection moulding
Technology and Applications of Metal Injection Moulding
Technology:
Metal Injection Moulding (MIM) combines plastic injection moulding and powdered metallurgy to produce high-strength, complex metal parts. The process starts with creating a feedstock by mixing metal powders with a binder, usually a thermoplastic polymer. This mixture is then injected into a mould, forming a “green part.” The binder is removed through thermal or chemical processes, leaving behind a porous metal structure known as the “brown part.” Finally, sintering at high temperatures densifies the metal, achieving its final shape and mechanical properties.
Applications:
1. Automotive Industry:
– Fuel Injectors: MIM produces fuel injectors with complex geometries and precise tolerances.
– Turbocharger Components: The process ensures high performance and durability under extreme conditions.
2. Medical and Dental:
– Orthodontic Braces: MIM creates small, intricate components with high strength.
– Surgical Instruments: Produces parts that require biocompatibility and corrosion resistance.
3. Consumer Electronics:
– Smartphone Components: Metal casings and connectors benefit from MIM’s ability to produce thin-walled, robust parts.
– Watch Components: Precision and aesthetics are enhanced using MIM technology.
4. Aerospace:
– Engine Components: Complex shapes and high-performance requirements are met effectively.
– Connectors and Fasteners: Lightweight yet strong parts are crucial for aerospace applications.
5. Industrial Tools:
– Cutting Tools: MIM provides the necessary hardness and wear resistance.
– Gear Components: Precision gears for machinery benefit from the fine detailing possible with MIM.
Advantages:
– Complexity: Can create complex geometries that are difficult to achieve with traditional methods.
– Material Efficiency: Reduces material waste compared to machining processes.
– Production Volume: Suitable for high-volume production runs, ensuring consistency and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion:
MIM is a versatile technology bridging the gap between conventional powder metallurgy and plastic injection moulding, providing unique benefits across various industries through its ability to produce intricate, high-performance metal parts.
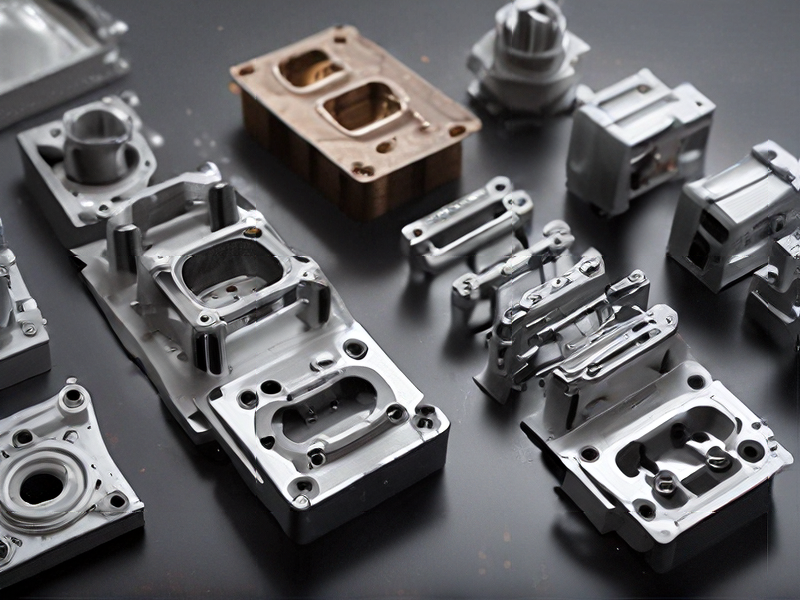

Quality Testing Methods for metal injection moulding and how to control quality
Quality testing in metal injection molding (MIM) involves several methods to ensure parts meet stringent standards. Key techniques include:
1. Material Analysis: Verify raw material composition using spectrometry and particle size analysis to ensure consistency and quality before production begins.
2. Dimensional Inspection: Use coordinate measuring machines (CMM) and optical comparators to check the dimensions of the molded parts against specifications.
3. Density Measurement: Measure part density using Archimedes’ principle or X-ray densitometry to detect porosity and ensure the integrity of the material.
4. Mechanical Testing: Conduct tensile, compression, and hardness tests to verify the mechanical properties of the finished parts meet required standards.
5. Surface Analysis: Inspect the surface finish using profilometers and visual inspections to detect defects such as cracks, voids, or surface irregularities.
6. Microstructure Examination: Use metallographic microscopy to examine the internal grain structure and phase distribution of the sintered parts to ensure proper sintering and absence of defects.
7. Non-destructive Testing (NDT): Apply methods like ultrasonic testing, X-ray, and dye penetrant testing to detect internal and surface defects without damaging the parts.
To control quality, implement these strategies:
– Statistical Process Control (SPC): Monitor production processes in real-time using SPC charts to detect and correct deviations before they result in defective parts.
– In-Process Inspections: Conduct regular inspections at various stages of the MIM process, from powder mixing to sintering, to catch and address issues early.
– Training and Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Ensure all operators are well-trained and follow detailed SOPs to maintain consistency in production.
– Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and analyze quality data to identify trends and areas for improvement, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
By employing these methods and controls, MIM manufacturers can maintain high quality and consistency in their products.
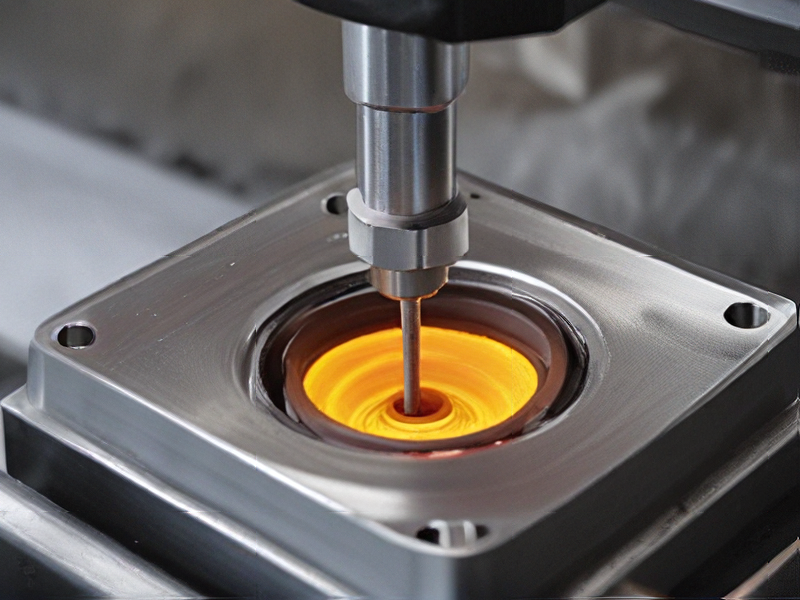

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from metal injection moulding
Tips for Procurement and Considerations When Purchasing from Metal Injection Moulding (MIM)
1. Supplier Evaluation:
– Experience and Expertise: Choose suppliers with proven experience in MIM, as this technology requires specialized knowledge.
– Quality Certifications: Look for ISO or other relevant quality certifications to ensure consistent product quality.
2. Material Selection:
– Material Properties: Ensure the selected material meets your application’s mechanical, thermal, and corrosion resistance requirements.
– Material Availability: Verify that the supplier can consistently provide the necessary materials to avoid supply chain disruptions.
3. Design Considerations:
– Complexity and Tolerances: MIM is suitable for complex geometries and tight tolerances. Ensure your design leverages these strengths.
– Size and Weight: Consider the size and weight of the parts, as MIM is most cost-effective for small, intricate components.
4. Cost Factors:
– Tooling Costs: Initial tooling costs for MIM can be high, but they are amortized over large production runs, reducing per-unit cost.
– Volume Requirements: MIM is ideal for high-volume production due to its ability to produce large quantities with minimal variation.
5. Quality Control:
– Inspection Capabilities: Ensure the supplier has robust inspection and testing capabilities, including X-ray, CMM, and metallographic analysis.
– Process Control: Check that the supplier maintains strict process controls to ensure part consistency.
6. Lead Times:
– Production Lead Time: Inquire about lead times for both prototype and full-scale production to align with your project timelines.
– Logistics and Shipping: Factor in logistics and shipping times, especially if sourcing internationally.
7. Sustainability:
– Environmental Impact: Assess the environmental practices of the supplier, including waste management and energy use.
– Recyclability: Consider the recyclability of the materials and the environmental footprint of the production process.
8. After-Sales Support:
– Technical Support: Ensure the supplier provides robust technical support and has a responsive customer service team.
– Warranty and Repairs: Clarify warranty terms and the process for handling defective parts or repairs.
By carefully considering these factors, you can optimize your procurement process and ensure high-quality, cost-effective MIM components.
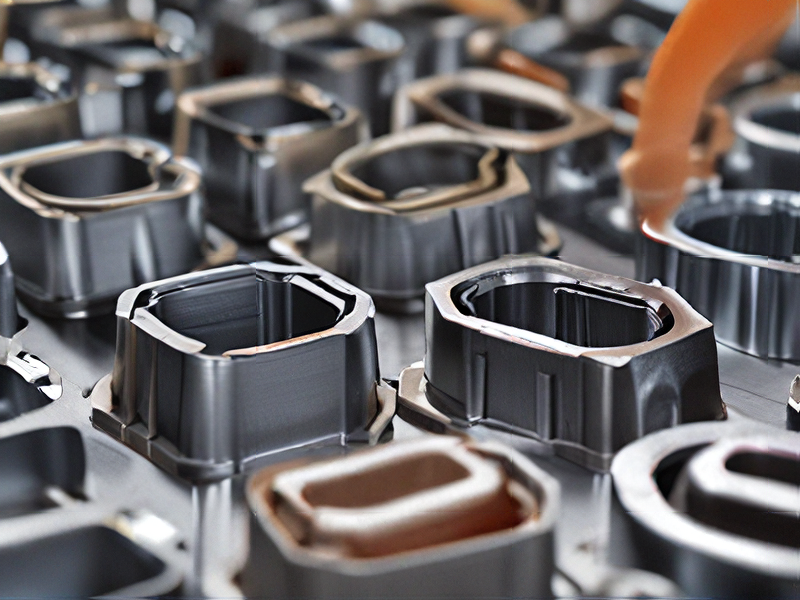

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from metal injection moulding in China
FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from Metal Injection Molding in China
1. What is Metal Injection Molding (MIM)?
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) is a manufacturing process that combines powder metallurgy and plastic injection molding to produce complex metal parts with high precision and excellent mechanical properties.
2. Why choose China for MIM manufacturing?
China offers competitive pricing, advanced manufacturing technology, skilled labor, and a robust supply chain infrastructure. These factors make it an attractive destination for MIM manufacturing.
3. What types of metals can be used in MIM?
Common metals used in MIM include stainless steel, titanium, copper, iron, and various alloys. The choice of material depends on the application’s requirements for strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
4. How do I select a reliable MIM manufacturer in China?
To select a reliable manufacturer, consider their experience, certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), production capacity, quality control processes, and client references. Visiting the facility and conducting audits can also provide valuable insights.
5. What are the typical applications of MIM parts?
MIM parts are used in various industries, including automotive, medical devices, aerospace, electronics, and consumer products, for components like gears, surgical instruments, connectors, and housings.
6. What is the lead time for MIM production in China?
Lead times can vary depending on the complexity and volume of the order. Generally, it ranges from a few weeks to several months, including time for tooling, production, and shipping.
7. How can I ensure the quality of MIM parts from China?
Ensure quality by working with manufacturers who have robust quality control systems, including material testing, dimensional inspection, and performance testing. Regular communication and quality audits are also crucial.
8. What are the cost factors in MIM manufacturing?
Key cost factors include material costs, tooling costs, production volume, complexity of the part, and secondary operations (e.g., surface finishing, heat treatment).
9. Are there any import/export regulations to consider?
Yes, ensure compliance with local regulations in both China and your home country, including tariffs, export controls, and customs documentation.
10. Can Chinese MIM manufacturers provide design and engineering support?
Many Chinese MIM manufacturers offer design and engineering support to optimize part design for manufacturability, cost-effectiveness, and performance.