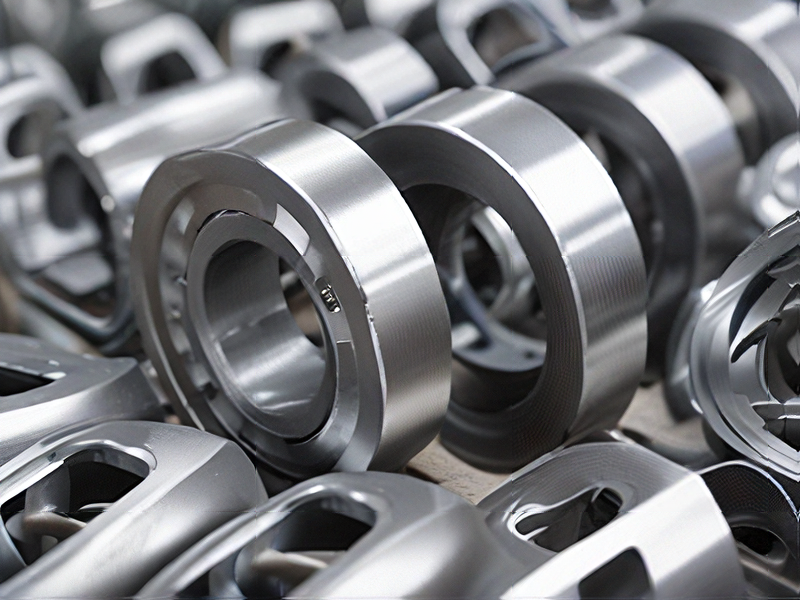
Technology and Applications of spin forming metal
Spin forming, also known as metal spinning or spin turning, is a metalworking process that shapes a flat metal disc into an axially symmetric part by rotating the disc and applying pressure with a tool. This technique is highly versatile and is used to create a variety of hollow, round shapes such as cones, cylinders, and hemispheres.
Technology
Spin forming involves several key steps:
1. Material Selection: Common materials include aluminum, stainless steel, and copper, chosen for their ductility and strength.
2. Setup: A flat metal disc is mounted on a lathe or spinning machine.
3. Forming: As the disc spins, a tool (roller or mandrel) presses against it, gradually shaping it over a form or mandrel.
4. Finishing: The part may be trimmed, heat-treated, or surface-finished to meet specific requirements.
Applications
1. Aerospace: Spin forming is used to produce rocket nose cones, satellite dishes, and jet engine components due to its ability to create lightweight and strong parts.
2. Automotive: The process manufactures components like hubcaps, gear blanks, and gas cylinders, emphasizing precision and durability.
3. Industrial: It creates large, robust parts such as pressure vessels, ventilation components, and machinery housings.
4. Consumer Goods: Items like cookware, lighting fixtures, and musical instruments benefit from the aesthetic and structural qualities of spin-formed metal.
Advantages
– Cost-Effective: Minimal material waste and low tooling costs compared to traditional stamping or forging.
– Flexibility: Suitable for both prototyping and mass production.
– Strength: Work hardening during the process increases the strength and durability of the final product.
– Precision: Capable of producing complex shapes with tight tolerances.
Spin forming combines technology and craftsmanship to deliver high-quality, efficient, and versatile metal parts across various industries.
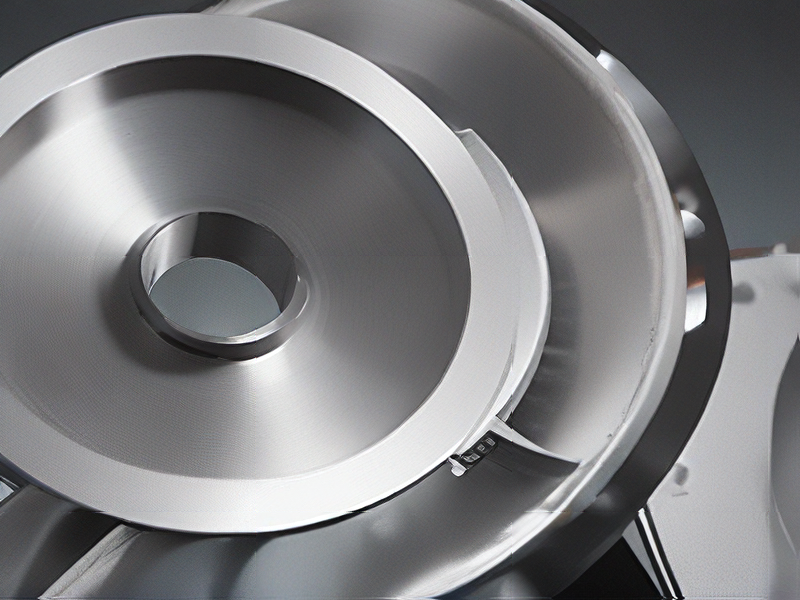
Quality Testing Methods for spin forming metal and how to control quality
Spin forming metal involves shaping metal sheets or tubes by rotating them and applying pressure to form desired shapes. To ensure quality, several testing methods can be employed:
1. Dimensional Inspection: Use calipers, micrometers, or coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) to verify dimensions against specifications.
2. Surface Inspection: Visual inspection or surface profilometers to check for imperfections like scratches, dents, or surface roughness.
3. Material Testing: Conduct hardness tests (e.g., Rockwell, Brinell) to ensure the metal meets required strength and durability standards.
4. Formability Testing: Assess material formability through tests like Erichsen cupping or deep drawing analysis to ensure it can withstand forming without defects.
5. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Use methods like ultrasonic testing (UT) or magnetic particle inspection (MPI) to detect internal defects without damaging the metal.
To control quality:
– Process Monitoring: Regularly monitor spinning parameters such as speed, pressure, and temperature to maintain consistency.
– Employee Training: Train operators on proper techniques and quality standards to minimize errors.
– Quality Management Systems (QMS): Implement QMS like ISO 9001 to ensure adherence to quality procedures and continuous improvement.
By employing these methods and controls, manufacturers can effectively ensure the quality of spun metal products, meeting customer expectations and industry standards.
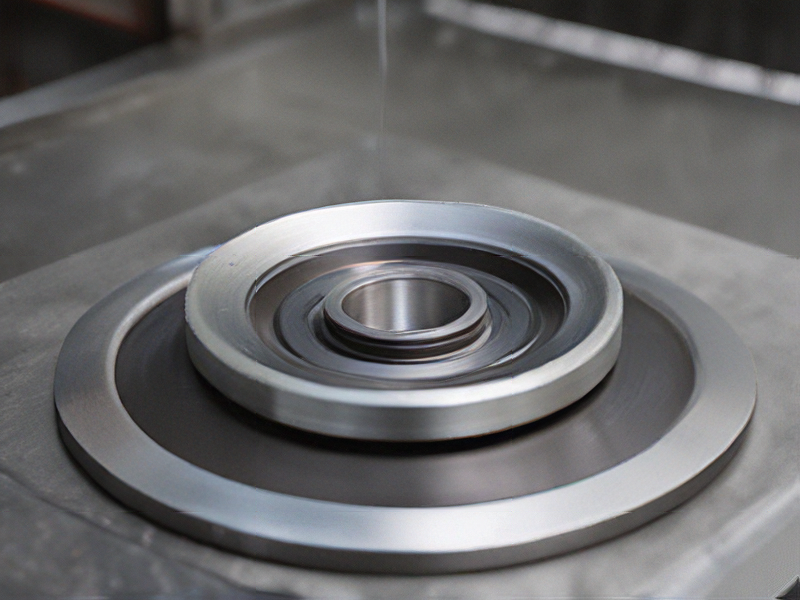

Tips for Procurement and Considerations when Purchasing from spin forming metal
When procuring spin-formed metal components, several key considerations can ensure quality, cost-efficiency, and timely delivery.
1. Material Selection: Choose the right material based on the application. Common metals used in spin forming include aluminum, steel, and titanium. Each material has unique properties affecting strength, weight, and corrosion resistance.
2. Supplier Expertise: Select suppliers with proven expertise in spin forming. Check their track record, certifications, and ability to handle the specific metals and complexities your project requires.
3. Design Specifications: Provide detailed design specifications, including dimensions, tolerances, and surface finish requirements. Precise specifications minimize errors and ensure the final product meets your needs.
4. Quality Control: Ensure the supplier has robust quality control processes, including inspections and testing protocols, to maintain consistent quality and detect defects early.
5. Cost Factors: Consider the total cost, including raw material prices, manufacturing costs, and any additional finishing processes. Volume discounts and long-term contracts can provide cost savings.
6. Lead Times: Evaluate the supplier’s production capacity and lead times. Early engagement and clear timelines can help manage project schedules and avoid delays.
7. Prototyping and Samples: Request prototypes or samples to assess the quality and compatibility with your design. This step can help identify potential issues before full-scale production.
8. Compliance and Standards: Ensure the supplier adheres to relevant industry standards and regulatory requirements. Compliance with standards like ISO can be a good indicator of quality.
9. Logistics and Shipping: Plan for logistics, including packaging, shipping methods, and costs. Proper packaging protects components during transit, reducing the risk of damage.
10. Sustainability: Consider the environmental impact of your procurement choices. Opt for suppliers that prioritize sustainable practices and materials.
By addressing these considerations, you can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of your procurement process for spin-formed metal components.
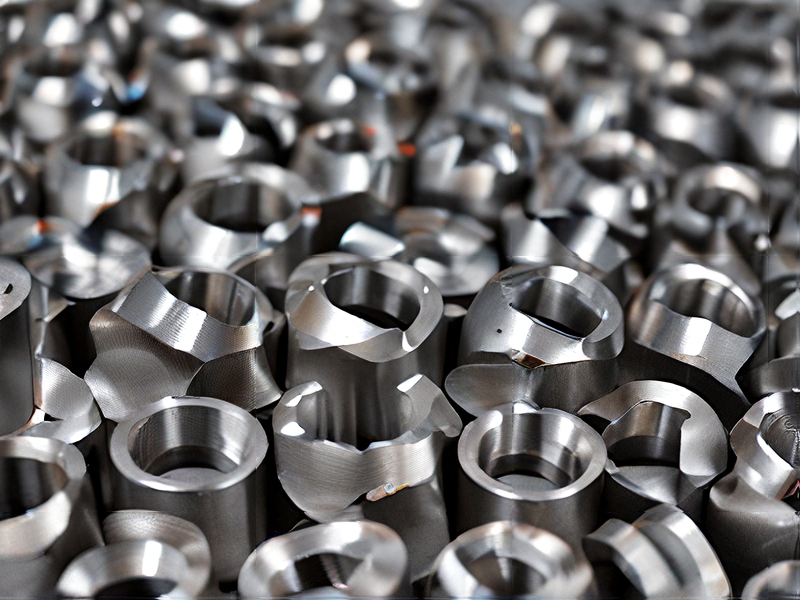

FAQs on Sourcing and Manufacturing from spin forming metal in China
When sourcing and manufacturing spin-formed metal components in China, several key FAQs arise:
1. What is spin forming?
Spin forming is a metalworking process where a metal disc or tube is rotated at high speed and formed into a desired shape using rollers or presses. It’s ideal for creating cylindrical or conical parts with high precision.
2. Why choose China for spin forming?
China offers competitive pricing due to lower labor costs and established infrastructure for manufacturing. It also has a wide range of suppliers experienced in various metalworking techniques.
3. How to select a reliable manufacturer?
Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in spin forming and metal fabrication. Verify their certifications, inspect their facilities if possible, and ask for client references to assess their quality and reliability.
4. What materials can be spin formed in China?
China can work with a variety of metals including aluminum, stainless steel, copper, and alloys. Ensure the manufacturer has experience with the specific material required for your project.
5. What are the typical lead times and costs?
Lead times vary based on complexity and order volume, but Chinese manufacturers generally offer competitive pricing and can accommodate both small and large production runs.
6. How to manage quality control?
Implement thorough quality control measures throughout the manufacturing process. Consider on-site inspections or third-party quality assurance services to ensure compliance with specifications.
7. What about intellectual property protection?
Protect your designs and intellectual property by working with manufacturers who respect confidentiality agreements. Consider legal protections and non-disclosure agreements where necessary.
By addressing these FAQs, businesses can navigate the complexities of spin forming metal sourcing and manufacturing in China effectively, ensuring quality outcomes and competitive advantages.

